Assessment of haemodynamic response to tracheal intubation and prone positioning following clonidine and enalaprilat in lumbar spine surgeries: A double blind randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 37601931
- PMCID: PMC10436731
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.ija_731_22
Assessment of haemodynamic response to tracheal intubation and prone positioning following clonidine and enalaprilat in lumbar spine surgeries: A double blind randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background and aim: This study evaluates the effectiveness of long-acting antihypertensive drugs (clonidine and enalaprilat) in blunting the intubation response. Also, the study seeks to determine how effectively clonidine and enalaprilat can maintain stable haemodynamics during a change in position.
Methods: After ethical committee approval and trial registration, a double-blinded, randomised controlled trial was conducted with 71 consenting patients scheduled for elective spine surgery in a prone position under general anaesthesia. Group C received clonidine 2 μg/kg, and Group E received enalaprilat 1.25 mg diluted in normal saline as an intravenous infusion given over 10 min before induction of anaesthesia. The changes in heart rate (HR) and blood pressure (BP) in response to the infusion of the study drugs, induction, tracheal intubation and change in position were recorded. P value <0.05 was considered significant. Statistical analysis was performed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 25.
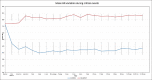
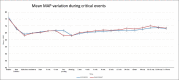
Results: Clonidine infusion caused a significant fall in heart rate post-infusion and post-induction with propofol (p value <0.05). Both clonidine and enalaprilat caused a significant fall in mean arterial pressure (MAP) post-infusion and post-induction (p value <0.05). Clonidine effectively blunted the intubation response with no increase in HR and MAP following intubation. Enalaprilat caused a significant rise in HR in response to intubation. On proning, there was a significant fall in MAP in both groups.
Conclusion: Clonidine is effective in blunting the intubation response. Preoperative infusion of clonidine and enalaprilat causes hypotension during a change of position.
Keywords: Clonidine; enalaprilat; haemodynamics; intubation; prone position; spine surgery.
Copyright: © 2023 Indian Journal of Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rajaprabu T, Kumar V. Comparison between the haemodynamic stability of dexmedetomidine and clonidine infusions among patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy- A randomised controlled trial. Indian J Clin Anaesth. 2019;6:437–40.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources