Genotyping and population characteristics of the China Kadoorie Biobank
- PMID: 37601966
- PMCID: PMC10435379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100361
Genotyping and population characteristics of the China Kadoorie Biobank
Abstract
The China Kadoorie Biobank (CKB) is a population-based prospective cohort of >512,000 adults recruited from 2004 to 2008 from 10 geographically diverse regions across China. Detailed data from questionnaires and physical measurements were collected at baseline, with additional measurements at three resurveys involving ∼5% of surviving participants. Analyses of genome-wide genotyping, for >100,000 participants using custom-designed Axiom arrays, reveal extensive relatedness, recent consanguinity, and signatures reflecting large-scale population movements from recent Chinese history. Systematic genome-wide association studies of incident disease, captured through electronic linkage to death and disease registries and to the national health insurance system, replicate established disease loci and identify 14 novel disease associations. Together with studies of candidate drug targets and disease risk factors and contributions to international genetics consortia, these demonstrate the breadth, depth, and quality of the CKB data. Ongoing high-throughput omics assays of collected biosamples and planned whole-genome sequencing will further enhance the scientific value of this biobank.
Keywords: GWAS; biobank; cardiovascular health; complex disease; genetic association studies; genetic epidemiology; genetics; genotyping; omics; prospective.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


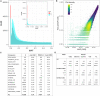
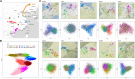
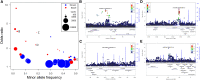
References
-
- Chen Z., Chen J., Collins R., Guo Y., Peto R., Wu F., Li L., China Kadoorie Biobank CKB collaborative group China Kadoorie Biobank of 0.5 million people: survey methods, baseline characteristics and long-term follow-up. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011;40:1652–1666. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyr120. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Millwood I.Y., Bennett D.A., Walters R.G., Clarke R., Waterworth D., Johnson T., Chen Y., Yang L., Guo Y., Bian Z., et al. A phenome-wide association study of a lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 loss-of-function variant in 90 000 Chinese adults. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016;45:1588–1599. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyw087. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

