Schizophrenia-associated somatic copy-number variants from 12,834 cases reveal recurrent NRXN1 and ABCB11 disruptions
- PMID: 37601975
- PMCID: PMC10435376
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100356
Schizophrenia-associated somatic copy-number variants from 12,834 cases reveal recurrent NRXN1 and ABCB11 disruptions
Abstract
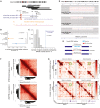
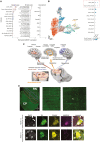
While germline copy-number variants (CNVs) contribute to schizophrenia (SCZ) risk, the contribution of somatic CNVs (sCNVs)-present in some but not all cells-remains unknown. We identified sCNVs using blood-derived genotype arrays from 12,834 SCZ cases and 11,648 controls, filtering sCNVs at loci recurrently mutated in clonal blood disorders. Likely early-developmental sCNVs were more common in cases (0.91%) than controls (0.51%, p = 2.68e-4), with recurrent somatic deletions of exons 1-5 of the NRXN1 gene in five SCZ cases. Hi-C maps revealed ectopic, allele-specific loops forming between a potential cryptic promoter and non-coding cis-regulatory elements upon 5' deletions in NRXN1. We also observed recurrent intragenic deletions of ABCB11, encoding a transporter implicated in anti-psychotic response, in five treatment-resistant SCZ cases and showed that ABCB11 is specifically enriched in neurons forming mesocortical and mesolimbic dopaminergic projections. Our results indicate potential roles of sCNVs in SCZ risk.
Keywords: ABCB11; NRXN1; genomics; mosaicism; schizophrenia; somatic; structural variants; treatment resistance.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Kirov G., Pocklington A.J., Holmans P., Ivanov D., Ikeda M., Ruderfer D., Moran J., Chambert K., Toncheva D., Georgieva L., et al. De novo CNV analysis implicates specific abnormalities of postsynaptic signalling complexes in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry. 2012;17:142–153. doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.154. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- U01 MH106883/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD105351/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH124393/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AG069446/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026880/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 MH129957/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH109501/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM144273/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG006855/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030463/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 ES030554/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG070921/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH104964/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T15 LM007092/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 AG072437/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103573/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH106575/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH106056/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH124602/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008313/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 AG058488/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH120269/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007544/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH124292/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK127405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119746/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS114226/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH121074/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH113715/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG051791/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

