Lobular Capillary Hemangioma Masquerading as Pyogenic Granuloma of Anterior Mandible: A Case Report
- PMID: 37602023
- PMCID: PMC10439000
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.42157
Lobular Capillary Hemangioma Masquerading as Pyogenic Granuloma of Anterior Mandible: A Case Report
Abstract
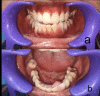
Pyogenic granuloma (PG) is a reactive connective tissue disorder with female predilection, which exhibits a tumor-like mass with occasional bleeding and superficial ulceration. It most commonly occurs in the maxillary gingiva followed by the mandibular gingiva. It can also occur in extra gingival sites like buccal mucosa, labial mucosa, and palate. There are two histopathological types of PG, namely, a lobular capillary hemangioma (LCH) variant and a non-LCH variant. The various management methods include surgical resection or laser excision along with deep curettage, and there are various nonsurgical methods like local steroid injection, topical administration of various drugs, and sclerotherapy. During the surgical excision, there is a risk of bleeding, and the surgeon should be equipped for the same. The PG (both LCH and non-LCH variant) has an increased chance of recurrence because of which complete excision is mandatory along with the removal of the local irritants. In this case report, a 28-year-old female patient reported recurrent painless swelling in the lower front gums for the past nine months. The surgical excision was done in-toto along with the removal of local irritants (calculus). The swelling was sent for histopathological examination. The patient was kept on regular follow-ups. The patient was followed up continuously for nine months. The swelling did not recur after the excision. Hence, it was concluded that complete excision and removal of local irritants are extremely crucial to prevent a recurrence.
Keywords: gingiva; lch; lobular capillary hemangioma; pyogenic granuloma; recurrent.
Copyright © 2023, Srinivedha et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Clinical and pathological differences between the PG and lobular capillary hemangioma in the oral cavity: a scoping review. Ver Berne J, Raubenheimer EJ, Jacobs R, Politis C. J Stomatol. 2020;73:206–216.
-
- Lobular capillary hemangioma of the oral mucosa: clinicopathological study of 43 cases with a special reference to immunohistochemical characterization of the vascular elements. Toida M, Hasegawa T, Watanabe F, et al. Pathol Int. 2003;53:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Lobular capillary hemangioma in a child: a case report and literature review. Mahajan A, Singhal P, Poonam Poonam. Open Access Sci Rep. 2012;1:265.
-
- Lobular capillary hemangioma (pyogenic granuloma) of the oral cavity. Thompson LD. Ear Nose Throat J. 2017;96:240. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
