A Retrospective Analysis of Clinico-Demographic and Genetic Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes in Isoniazid Mono-Resistant Tuberculosis Patients: A Single-Center Study
- PMID: 37602046
- PMCID: PMC10439306
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.42166
A Retrospective Analysis of Clinico-Demographic and Genetic Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes in Isoniazid Mono-Resistant Tuberculosis Patients: A Single-Center Study
Abstract
Introduction: Treatment failure and relapse rates are more likely to occur when there is isoniazid (INH) resistance. So, we can no longer ignore the problem of isoniazid mono-resistance. It is pertinent to control the spread of primary INH resistance and prevent secondary resistance.
Aim: This study aims to evaluate subjects' clinical, demographic, and genetic characteristics and explore their treatment outcomes.
Methods: All data of isoniazid mono-resistant tuberculosis (TB) patients, which were maintained in the electronic database of mandatory notifications (NIKSHAY Portal) between 2017 and 2022, were reviewed. A total of 54 patients were included after excluding five patients with ongoing treatment.
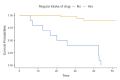
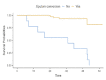
Results: Of 54 patients, 41 (75.9%) were cured, which was classified under favorable outcome, and the rest were classified under unfavorable outcome. Phenotypic, high-level mutation (katG) was found in 48 (88.9%) patients. Kaplan-Meier curves show that survival probabilities increase in weeks with regular intake of drugs.
Conclusion: Our study found that those with younger ages and males were more affected. We found favorable outcomes in the majority of patients.
Keywords: clinical characteristics; demographic characteristics; genetic mutation characteristics; mono-resistant; successful treatment outcome; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2023, Hymn et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Ministry of Health and Welfare (India) Cent TB Div Heal Welf India. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Central TB Division; 2021. Guidelines for programmatic management of drug resistant tuberculosis in India-2021; pp. 45–54.
-
- Isoniazid mono-resistant tuberculosis: time to take it seriously. Garg K, Saini V, Dhillon R, Agarwal P. Indian J Tuberc. 2019;66:247–252. - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Government of India; 2016. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India: National anti-TB drug resistance survey.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
