Ten-year follow-up of corneal cross-linking and refractive surface ablation in patients with asymmetric corneal topography
- PMID: 37602610
- PMCID: PMC10565913
- DOI: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_2557_22
Ten-year follow-up of corneal cross-linking and refractive surface ablation in patients with asymmetric corneal topography
Abstract
Purpose: Compare the safety and efficacy of wavefront-guided photorefractive keratotomy (PRK) 6 months after cross-linking (CXL) to wavefront-guided PRK alone for refractive correction in patients with bilateral asymmetric corneal topography.
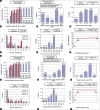
Methods: Prospective randomized clinical trial with 16 patients (32 eyes). CXL with subsequent PRK after 6 months in one eye, and PRK alone was performed in contralateral eyes. The follow-up was 10 years. We analyzed visual outcomes, Scheimpflug topography, and corneal haze evaluation.
Results: Eyes in the PRK group showed better results than in the CXL + PRK group. Mean postoperative CDVA was 0.044 logmar (SD, 0.073) in the PRK group and 0.1 logmar (SD, 0.21) in the CXL + PRK group, the mean sphere was + 0.21 (SD, 0.6) D in the PRK group and 0.87 (SD, 2.3) D in the CXL + PRK group, and mean SE was -0.35 (SD, 0.65) D in the PRK group and 0.62 (SD, 2.32) D in the CXL + PRK group. In one patient, a steepening of 2.5 D and a thinning of 17 μm occurred in PRK alone group. Two patients in the CXL + PRK group presented corneal haze. The overall complication rate was 18,75% (haze and ectasia).
Conclusion: Non-simultaneous CXL and PRK procedures yielded good refractive results, but worse than those obtained with PRK alone. Although one patient in the PRK group developed corneal ectasia, the CXL + PRK group had a higher loss of vision lines, indicating less safety.
Keywords: Cornea; corneal stroma; corneal topography; excimer; lasers; photorefractive keratectomy; refractive surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two-year follow-up of corneal cross-linking and refractive surface ablation in patients with asymmetric corneal topography.Br J Ophthalmol. 2019 Jan;103(1):137-142. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2017-310840. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 29610222 Clinical Trial.
-
Non-topography-guided PRK combined with CXL for the correction of refractive errors in patients with early stage keratoconus.J Refract Surg. 2014 Oct;30(10):688-93. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20140903-02. J Refract Surg. 2014. PMID: 25291752
-
Comparison of sequential vs same-day simultaneous collagen cross-linking and topography-guided PRK for treatment of keratoconus.J Refract Surg. 2009 Sep;25(9):S812-8. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20090813-10. Epub 2009 Sep 11. J Refract Surg. 2009. PMID: 19772257
-
Review of Laser Vision Correction (LASIK, PRK and SMILE) with Simultaneous Accelerated Corneal Crosslinking - Long-term Results.Curr Eye Res. 2019 Nov;44(11):1171-1180. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2019.1656749. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Curr Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 31411927 Review.
-
Outcomes of Simultaneous and Sequential Cross-linking With Excimer Laser Surface Ablation in Keratoconus.J Refract Surg. 2018 Oct 1;34(10):690-696. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20180824-01. J Refract Surg. 2018. PMID: 30296330
Cited by
-
New approaches of intracorneal ring segments implantation for asymmetric keratoconus treatment: A case series.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 1;73(7):1079-1083. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_1452_24. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40586198 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dawson DG, Randleman JB, Grossniklaus HE, O'Brien TP, Dubovy SR, Schmack I, et al. Corneal ectasia after excimer laser keratorefractive surgery: Histopathology, ultrastructure, and pathophysiology. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:2181–91.e1. - PubMed
-
- Randleman JB, Woodward M, Lynn MJ, Stulting RD. Risk assessment for ectasia after corneal refractive surgery. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:37–50. - PubMed
-
- Wollensak G, Spoerl E, Seiler T. Riboflavin/ultraviolet-a-induced collagen crosslinking for the treatment of keratoconus. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003;135:620–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

