When does humoral memory enhance infection?
- PMID: 37603552
- PMCID: PMC10470880
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011377
When does humoral memory enhance infection?
Abstract
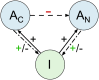
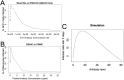
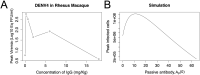
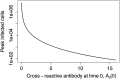
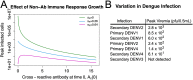
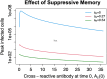
Antibodies and humoral memory are key components of the adaptive immune system. We consider and computationally model mechanisms by which humoral memory present at baseline might increase rather than decrease infection load; we refer to this effect as EI-HM (enhancement of infection by humoral memory). We first consider antibody dependent enhancement (ADE) in which antibody enhances the growth of the pathogen, typically a virus, and typically at intermediate 'Goldilocks' levels of antibody. Our ADE model reproduces ADE in vitro and enhancement of infection in vivo from passive antibody transfer. But notably the simplest implementation of our ADE model never results in EI-HM. Adding complexity, by making the cross-reactive antibody much less neutralizing than the de novo generated antibody or by including a sufficiently strong non-antibody immune response, allows for ADE-mediated EI-HM. We next consider the possibility that cross-reactive memory causes EI-HM by crowding out a possibly superior de novo immune response. We show that, even without ADE, EI-HM can occur when the cross-reactive response is both less potent and 'directly' (i.e. independently of infection load) suppressive with regard to the de novo response. In this case adding a non-antibody immune response to our computational model greatly reduces or completely eliminates EI-HM, which suggests that 'crowding out' is unlikely to cause substantial EI-HM. Hence, our results provide examples in which simple models give qualitatively opposite results compared to models with plausible complexity. Our results may be helpful in interpreting and reconciling disparate experimental findings, especially from dengue, and for vaccination.
Copyright: © 2023 Nikas et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Chau TNB, Quyen NTH, Thuy TT, Tuan NM, Hoang DM, Dung NTP, et al. Dengue in Vietnamese infants—results of infection-enhancement assays correlate with age-related disease epidemiology, and cellular immune responses correlate with disease severity. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2008;198(4):516–524. doi: 10.1086/590117 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

