Kar4, the yeast homolog of METTL14, is required for mRNA m6A methylation and meiosis
- PMID: 37603553
- PMCID: PMC10470960
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010896
Kar4, the yeast homolog of METTL14, is required for mRNA m6A methylation and meiosis
Abstract
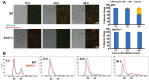
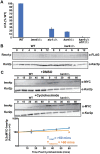
KAR4, the yeast homolog of the mammalian mRNA N6A-methyltransferase complex component METTL14, is required for two disparate developmental programs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: mating and meiosis. To understand KAR4's role in yeast mating and meiosis, we used a genetic screen to isolate 25 function-specific mutant alleles, which map to non-overlapping surfaces on a predicted structure of the Kar4 protein (Kar4p). Most of the mating-specific alleles (Mat-) abolish Kar4p's interaction with the transcription factor Ste12p, indicating that Kar4p's mating function is through Ste12p. In yeast, the mRNA methyltransferase complex was previously defined as comprising Ime4p (Kar4p's paralog and the homolog of mammalian METTL3), Mum2p (homolog of mammalian WTAP), and Slz1p (MIS), but not Kar4p. During meiosis, Kar4p interacts with Ime4p, Mum2p, and Slz1p. Moreover, cells lacking Kar4p have highly reduced levels of mRNA methylation during meiosis indicating that Kar4p is a key member of the methyltransferase complex, as it is in humans. Analysis of kar4Δ/Δ and 7 meiosis-specific alleles (Mei-) revealed that Kar4p is required early in meiosis, before initiation of S-phase and meiotic recombination. High copy expression of the meiotic transcriptional activator IME1 rescued the defect of these Mei- alleles. Surprisingly, Kar4p was also found to be required at a second step for the completion of meiosis and sporulation. Over-expression of IME1 in kar4Δ/Δ permits pre-meiotic S-phase, but most cells remained arrested with a monopolar spindle. Analysis of the function-specific mutants revealed that roughly half became blocked after premeiotic DNA synthesis and did not sporulate (Spo-). Loss of Kar4p's Spo function was suppressed by overexpression of RIM4, a meiotic translational regulator. Overexpression of IME1 and RIM4 together allowed sporulation of kar4Δ/Δ cells. Taken together, these data suggest that Kar4p regulates meiosis at multiple steps, presumably reflecting requirements for methylation in different stages of meiotic gene expression.
Copyright: © 2023 Park et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






Update of
-
Kar4, the Yeast Homolog of METTL14, is Required for mRNA m 6 A Methylation and Meiosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 29:2023.01.29.526094. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.29.526094. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Genet. 2023 Aug 21;19(8):e1010896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010896. PMID: 36747717 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

