Targeted Inhibition of lncRNA Malat1 Alters the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Preclinical Syngeneic Mouse Models of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 37603945
- PMCID: PMC10618655
- DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-23-0045
Targeted Inhibition of lncRNA Malat1 Alters the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Preclinical Syngeneic Mouse Models of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
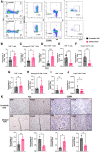
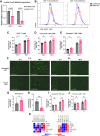
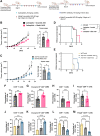
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNA) play an important role in gene regulation in both normal tissues and cancer. Targeting lncRNAs is a promising therapeutic approach that has become feasible through the development of gapmer antisense oligonucleotides (ASO). Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript (Malat1) is an abundant lncRNA whose expression is upregulated in several cancers. Although Malat1 increases the migratory and invasive properties of tumor cells, its role in the tumor microenvironment (TME) is still not well defined. We explored the connection between Malat1 and the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) using several immune-competent preclinical syngeneic Tp53-null triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) mouse models that mimic the heterogeneity and immunosuppressive TME found in human breast cancer. Using a Malat1 ASO, we were able to knockdown Malat1 RNA expression resulting in a delay in primary tumor growth, decreased proliferation, and increased apoptosis. In addition, immunophenotyping of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes revealed that Malat1 inhibition altered the TIME, with a decrease in immunosuppressive tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) as well as an increase in cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. Malat1 depletion in tumor cells, TAMs, and MDSCs decreased immunosuppressive cytokine/chemokine secretion whereas Malat1 inhibition in T cells increased inflammatory secretions and T-cell proliferation. Combination of a Malat1 ASO with chemotherapy or immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) improved the treatment responses in a preclinical model. These studies highlight the immunostimulatory effects of Malat1 inhibition in TNBC, the benefit of a Malat1 ASO therapeutic, and its potential use in combination with chemotherapies and immunotherapies.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes proliferation and invasion via targeting miR-129-5p in triple-negative breast cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Nov;95:922-928. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.005. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28915533
-
Reciprocal regulation of Hsa-miR-1 and long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer development.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):7383-94. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4605-6. Epub 2015 Dec 16. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26676637
-
Functional and prognostic significance of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 as a metastasis driver in ER negative lymph node negative breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 28;7(26):40418-40436. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9622. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27250026 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic significance of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Apr;1875(2):188502. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188502. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33428963 Review.
-
Functional roles of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 in gynecologic cancers.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Jan;25(1):48-65. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-02914-8. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36042115 Review.
Cited by
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs as Regulators for Targeting Breast Cancer Stem Cells and Tumor Immune Microenvironment: Biological Properties and Therapeutic Potential.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;16(2):290. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020290. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction and validation of immune-associated lncRNA model for predicting immune status and therapeutic reactions of triple-negative breast cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Sep 15;16(9):4355-4378. doi: 10.62347/VIXN9362. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39398616 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the role of non-coding RNAs in prostate cancer progression: exploring the interplay with the Wnt signaling pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 27;14:1269233. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1269233. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37829301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC01235 is an Upstream Regulator of the NFIB Gene and the NOTCH Pathway in Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 30:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-24-1143. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-24-1143. Online ahead of print. Mol Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40586711
-
Deciphering the code: the pivotal role of lncRNAs in advancing TNBC therapy.Front Oncol. 2024 Sep 2;14:1450980. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1450980. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39286016 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

