Deep venous thrombosis post mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischaemic stroke
- PMID: 37604593
- PMCID: PMC10445379
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2023-255391
Deep venous thrombosis post mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischaemic stroke
Abstract
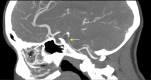
A woman in her 20s presented with neck pain, slurred speech and left-sided weakness. She successfully underwent mechanical thrombectomy (MT) for total occlusion of the basilar artery and made full neurological recovery. Initial ultrasound Doppler of legs (USDL) did not show any deep vein thrombosis (DVT). However, 2 days later, a repeat USDL revealed an extensive proximal DVT in the right common femoral vein. CT scan confirmed a haematoma arising from the femoral access site causing compression of the adjacent common femoral vein. This may have initiated DVT formation or exacerbated extension of a previously undetected DVT. Echocardiogram revealed a patent foramen ovale. As the patient was asymptomatic, delayed or missed diagnosis of DVT would have put her at risk of life-threatening pulmonary embolism or further strokes. Clinicians should maintain a high index of suspicion of DVT as a direct procedural complication from MT so treatment can be initiated promptly.
Keywords: Interventional radiology; Stroke; Venous thromboembolism.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2023. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Filis K, Arhontovasilis F, Theodorou D, et al. Management of early and late detected vascular complications following femoral arterial puncture for cardiac catheterization. Hellenic J Cardiol 2007;48:134–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
