CD36 mediates SARS-CoV-2-envelope-protein-induced platelet activation and thrombosis
- PMID: 37604832
- PMCID: PMC10442425
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-40824-7
CD36 mediates SARS-CoV-2-envelope-protein-induced platelet activation and thrombosis
Abstract
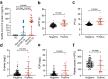
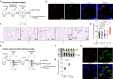
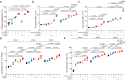
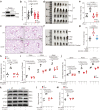
Aberrant coagulation and thrombosis are associated with severe COVID-19 post-SARS-CoV-2 infection, yet the underlying mechanism remains obscure. Here we show that serum levels of SARS-CoV-2 envelope (E) protein are associated with coagulation disorders of COVID-19 patients, and intravenous administration of the E protein is able to potentiate thrombosis in mice. Through protein pull-down and mass spectrometry, we find that CD36, a transmembrane glycoprotein, directly binds with E protein and mediates hyperactivation of human and mouse platelets through the p38 MAPK-NF-κB signaling pathway. Conversely, the pharmacological blockade of CD36 or p38 notably attenuates human platelet activation induced by the E protein. Similarly, the genetic deficiency of CD36, as well as the pharmacological inhibition of p38 in mice, significantly diminishes E protein-induced platelet activation and thrombotic events. Together, our study reveals a critical role for the CD36-p38 axis in E protein-induced platelet hyperactivity, which could serve as an actionable target for developing therapies against aberrant thrombotic events related to the severity and mortality of COVID-19.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 9) Enhances Platelet Activation, Thrombosis, and Myocardial Infarct Expansion by Binding to Platelet CD36.Circulation. 2021 Jan 5;143(1):45-61. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046290. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Circulation. 2021. PMID: 32988222
-
Platelet CD36 promotes thrombosis by activating redox sensor ERK5 in hyperlipidemic conditions.Blood. 2017 May 25;129(21):2917-2927. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-11-750133. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28336528 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet CD36 mediates interactions with endothelial cell-derived microparticles and contributes to thrombosis in mice.J Clin Invest. 2008 May;118(5):1934-43. doi: 10.1172/JCI34904. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18431509 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of CD36/GPIV in Platelet Biology.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2024 Mar;50(2):224-235. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1768935. Epub 2023 May 16. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2024. PMID: 37192651 Review.
-
Platelets and SARS-CoV-2 During COVID-19: Immunity, Thrombosis, and Beyond.Circ Res. 2023 May 12;132(10):1272-1289. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321930. Epub 2023 May 11. Circ Res. 2023. PMID: 37167360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developing inhibitory peptides against SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein.PLoS Biol. 2024 Mar 14;22(3):e3002522. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002522. eCollection 2024 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38483887 Free PMC article.
-
The SARS-CoV-2 envelope PDZ binding motif acts as a virulence factor disrupting host's epithelial cell-cell junctions.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jul 11;30(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00758-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40646464 Free PMC article.
-
m6A-modified circCacna1c regulates necroptosis and ischemic myocardial injury by inhibiting Hnrnpf entry into the nucleus.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Nov 12;29(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00649-8. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39533214 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Cysteine Oxidation in Thrombotic Disorders.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jan 9;13(1):83. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010083. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebromicrovascular mechanisms contributing to long COVID: implications for neurocognitive health.Geroscience. 2025 Feb;47(1):745-779. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01487-4. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 39777702 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO. WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. 2022. https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed September 17, 2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

