MacroH2A restricts inflammatory gene expression in melanoma cancer-associated fibroblasts by coordinating chromatin looping
- PMID: 37605008
- PMCID: PMC10495263
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-023-01208-7
MacroH2A restricts inflammatory gene expression in melanoma cancer-associated fibroblasts by coordinating chromatin looping
Abstract
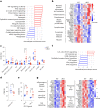
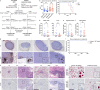
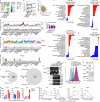
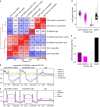
MacroH2A has established tumour suppressive functions in melanoma and other cancers, but an unappreciated role in the tumour microenvironment. Using an autochthonous, immunocompetent mouse model of melanoma, we demonstrate that mice devoid of macroH2A variants exhibit increased tumour burden compared with wild-type counterparts. MacroH2A-deficient tumours accumulate immunosuppressive monocytes and are depleted of functional cytotoxic T cells, characteristics consistent with a compromised anti-tumour response. Single cell and spatial transcriptomics identify increased dedifferentiation along the neural crest lineage of the tumour compartment and increased frequency and activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts following macroH2A loss. Mechanistically, macroH2A-deficient cancer-associated fibroblasts display increased myeloid chemoattractant activity as a consequence of hyperinducible expression of inflammatory genes, which is enforced by increased chromatin looping of their promoters to enhancers that gain H3K27ac. In summary, we reveal a tumour suppressive role for macroH2A variants through the regulation of chromatin architecture in the tumour stroma with potential implications for human melanoma.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

