Association of the androgens with COVID-19 prognostic outcomes: a systematic review
- PMID: 37605265
- PMCID: PMC10440898
- DOI: 10.1186/s13690-023-01168-2
Association of the androgens with COVID-19 prognostic outcomes: a systematic review
Abstract
Objective: The coronavirus disease 2019 was a global public health emergency in later years (from 2020 to early 2022), and androgens have been associated with infection and prognostic outcomes. However, the relationship between low serum testosterone levels and prognostic outcomes remains inconclusive. This systematic review aimed to investigate the relationship between serum testosterone levels and prognostic outcomes in patients with COVID-19.
Methods: We searched PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE and Web of Science electronic databases for all literature from January 1, 2020, to September 1, 2022. In addition, we also searched literature manually. The search terms were COVID-19, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), androgens, and testosterone. There were no language restrictions for retrieval.
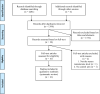
Results: Our search identified 2285 articles, resulting in a full-text analysis of 16 studies, including 12 cohort studies and four case-control studies. Low serum testosterone levels were observed to be statistically associated with a higher probability of intensive care unit (ICU) admission in seven studies. In eight studies, higher hospital mortality was associated with lower serum testosterone levels. Six studies found that low serum testosterone levels were associated with a statistically significant difference in lung function impairment. Only four studies found that among living patients, those with lower serum testosterone levels had longer hospital stays. All but one of the included studies had a low risk of bias.
Conclusions: Based on available data, low serum testosterone levels are associated with higher rates of ICU admission, hospital mortality, risk of lung failure, inflammatory markers, and longer hospital stays in patients with COVID-19 compared with those having normal serum testosterone levels.
Keywords: Androgens; COVID-19; Public health emergency; Systematic review; Testosterone.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 14;5(5):CD013600. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013600. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 10;7:CD013600. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub2. PMID: 32406927 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Severely low testosterone in males with COVID-19: A case-control study.Andrology. 2021 Jul;9(4):1043-1052. doi: 10.1111/andr.12993. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Andrology. 2021. PMID: 33635589 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of serum total testosterone and its relationship with other laboratory parameters on the prognosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in SARS-CoV-2 infected male patients: a cohort study.Aging Male. 2020 Dec;23(5):1493-1503. doi: 10.1080/13685538.2020.1807930. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Aging Male. 2020. PMID: 32883151
-
The Complex Interplay between Serum Testosterone and the Clinical Course of Coronavirus Disease 19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review of Clinical and Preclinical Evidence.World J Mens Health. 2023 Jul;41(3):466-481. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.220143. Epub 2023 Jan 3. World J Mens Health. 2023. PMID: 36649920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
Cited by
-
Testosterone Replacement Therapy and Risk of COVID-19 and Effect of COVID-19 on Testosterone's Treatment Effect.J Endocr Soc. 2025 Feb 5;9(3):bvaf002. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaf002. eCollection 2025 Feb 4. J Endocr Soc. 2025. PMID: 39911523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus Disease (Covid-19) Dashboard. 2023 February 22, 2023 February 22, 2023]; Available from: Available at: https://covid19.who.int.
-
- Thunders M. and B. Delahunt Gene of the month: TMPRSS2 (transmembrane serine protease 2). J Clin Pathol, 2020, 7312: 773. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous