Recent Progress in Antibody Epitope Prediction
- PMID: 37606436
- PMCID: PMC10443277
- DOI: 10.3390/antib12030052
Recent Progress in Antibody Epitope Prediction
Abstract
Recent progress in epitope prediction has shown promising results in the development of vaccines and therapeutics against various diseases. However, the overall accuracy and success rate need to be improved greatly to gain practical application significance, especially conformational epitope prediction. In this review, we examined the general features of antibody-antigen recognition, highlighting the conformation selection mechanism in flexible antibody-antigen binding. We recently highlighted the success and warning signs of antibody epitope predictions, including linear and conformation epitope predictions. While deep learning-based models gradually outperform traditional feature-based machine learning, sequence and structure features still provide insight into antibody-antigen recognition problems.
Keywords: antibody; antibody design; artificial intelligence; epitope.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
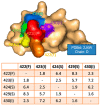
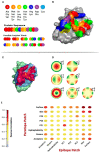

References
-
- Liu J., Yang S., Cao B., Zhou G., Zhang F., Wang Y., Wang R., Zhu L., Meng Y., Hu C., et al. Targeting B7-H3 via chimeric antigen receptor T cells and bispecific killer cell engagers augments antitumor response of cytotoxic lymphocytes. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021;14:21. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-01024-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu L., Liu J., Zhou G., Ng H.M., Ang I.L., Ma G., Liu Y., Yang S., Zhang F., Miao K., et al. Targeting immune checkpoint B7-H3 antibody-chlorin e6 bioconjugates for spectroscopic photoacoustic imaging and photodynamic therapy. Chem. Commun. 2019;55:14255–14258. doi: 10.1039/C9CC06839B. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cao B., Liu M., Wang L., Zhu K., Cai M., Chen X., Feng Y., Yang S., Fu S., Zhi C., et al. Remodelling of tumour microenvironment by microwave ablation potentiates immunotherapy of AXL-specific CAR T cells against non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022;13:6203. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33968-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

