Characterization of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for Quantification of Antibodies against Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Enteritidis O-Antigens in Human Sera
- PMID: 37606441
- PMCID: PMC10443281
- DOI: 10.3390/biotech12030054
Characterization of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for Quantification of Antibodies against Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Enteritidis O-Antigens in Human Sera
Abstract
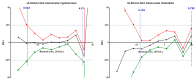
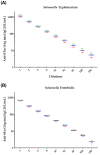
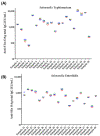
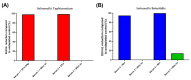
Nontyphoidal Salmonella (NTS) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality caused by enteric pathogens worldwide in both children and adults, and vaccines are not yet available. The measurement of antigen-specific antibodies in the sera of vaccinated or convalescent individuals is crucial to understand the incidence of disease and the immunogenicity of vaccine candidates. A solid and standardized assay used to determine the level of specific anti-antigens IgG is therefore of paramount importance. In this work, we presented the characterization of a customized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with continuous readouts and a standardized definition of EU/mL. We assessed various performance parameters: standard curve accuracy, dilutional linearity, intermediate precision, specificity, limits of blanks, and quantification. The simplicity of the assay, its high sensitivity and specificity coupled with its low cost and the use of basic consumables and instruments without the need of high automation makes it suitable for transfer and application to different laboratories, including resource-limiting settings where the disease is endemic. This ELISA is, therefore, fit for purpose to be used for quantification of antibodies against Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Enteritidis O-antigens in human samples, both for vaccine clinical trials and large sero-epidemiological studies.
Keywords: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA); Generalized Modules for Membrane Antigens (GMMA); antibodies; human sera; iNTS; non-typhoidal Salmonella; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
M.G.A., D.D.S., M.I.-G., M.P., F.B.S., R.C. and O.R. are or were employed by the GSK group of companies at the time in which the study was conducted. GSK Vaccines Institute for Global Health Srl is an affiliate of GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA. This does not alter the authors’ adherence to all journal policies on data and material sharing.
Figures

References
-
- Bula-Rudas F.J., Rathore M.H., Maraqa N.F. Salmonella Infections in Childhood. Adv. Pediatr. 2015;62:29–58. - PubMed
-
- Kariuki S., Revathi G., Kariuki N., Kiiru J., Mwituria J., Muyodi J., Githinji J.W., Kagendo D., Munyalo A., Hart C.A. Invasive multidrug-resistant non-typhoidal Salmonella infections in Africa: Zoonotic or anthroponotic transmission? Pt 5J. Med. Microbiol. 2006;55:585–591. - PubMed
-
- Tennant S.M., MacLennan C.A., Simon R., Martin L.B., Khan M.I. Nontyphoidal salmonella disease: Current status of vaccine research and development. Vaccine. 2016;34:2907–2910. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
