Real-World Utilization of Molnupiravir during the COVID-19 Omicron Surge in Israel
- PMID: 37606468
- PMCID: PMC10443270
- DOI: 10.3390/epidemiologia4030031
Real-World Utilization of Molnupiravir during the COVID-19 Omicron Surge in Israel
Abstract
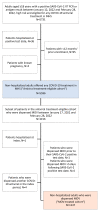
Molnupiravir (MOV) was introduced in Israel in January 2022 during the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron surge for high-risk patients contraindicated for nirmatrelvir/ritonavir. This retrospective cohort study aimed to describe characteristics of patients offered COVID-19 antiviral treatment in Maccabi Healthcare Services (antiviral treatment-eligible cohort; n = 5596) between 12 January and 28 February 2022, and the subset of these who were dispensed MOV (MOV-treated cohort; n = 1147), as well as outcomes following MOV dispensation. Median (interquartile range) age in the antiviral treatment-eligible and MOV-treated cohorts were 70.5 (61.1, 77.3) and 74.1 (64.3, 81.7) years, respectively. The MOV-treated cohort (male: 53.2%) had high rates of COVID-19 vaccination (91.4%) and comorbidities, including immunosuppression (40.0%) and chronic kidney disease (67.0%; eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2: 28.8%), and most used comedications either contraindicated or with major potential for drug-drug interactions with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (87.3%). At 28 days post-MOV dispensation, the cumulative incidence (95% CI) of COVID-19-related hospitalization and/or all-cause mortality was 3.6% (2.5%, 4.6%), with similar rates across sexes and age groups (18-64 vs. ≥65 years), and lower rates among recently vaccinated and/or recently SARS-CoV-2-infected patients. These data describe the characteristics and outcomes for MOV-treated patients in Israel, whose clinical characteristics may preclude the use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir to treat their COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; molnupiravir.
Conflict of interest statement
Tobias Bergroth, Anna Eisenberg, and Yohance Omar Whiteside are employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, and are shareholders in Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. Lilac Tene, Clara Weil, and Gabriel Chodick declare no conflicts of interest. Yoseph Caraco acted as the Principal Investigator in the MOVe-OUT trial conducted at The Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of All-Cause Hospitalization and Death Among Nonhospitalized Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and SARS-CoV-2 Infection Treated With Molnupiravir or Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir During the Omicron Wave in Hong Kong.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 May 1;6(5):e2314393. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.14393. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37204790 Free PMC article.
-
Molnupiravir Use Among Patients with COVID-19 in Real-World Settings: A Systematic Literature Review.Infect Dis Ther. 2024 Jun;13(6):1177-1198. doi: 10.1007/s40121-024-00976-5. Epub 2024 May 14. Infect Dis Ther. 2024. PMID: 38743192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nirmatrelvir or Molnupiravir Use and Severe Outcomes From Omicron Infections.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Sep 5;6(9):e2335077. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.35077. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37733342 Free PMC article.
-
Real-life comparison of mortality in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection at risk for clinical progression treated with molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir during the Omicron era in Italy: a nationwide, cohort study.Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2023 Jul 14;31:100684. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2023.100684. eCollection 2023 Aug. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2023. PMID: 37547273 Free PMC article.
-
Molnupiravir and Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir: Oral Coronavirus Disease 2019 Antiviral Drugs.Clin Infect Dis. 2023 Jan 6;76(1):165-171. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac180. Clin Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 35245942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of COVID-19 patient outcomes with molnupiravir treatment and the role of risk factors: a single-centre retrospective descriptive study.Cent Eur J Public Health. 2024 Dec;32(Supplement):104-110. doi: 10.21101/cejph.a8398. Cent Eur J Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39832155
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous