A Mixture of Essential Oils from Three Cretan Aromatic Plants Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Proliferation: A Proof-of-Concept Intervention Study in Ambulatory Patients
- PMID: 37606476
- PMCID: PMC10443288
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases11030105
A Mixture of Essential Oils from Three Cretan Aromatic Plants Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Proliferation: A Proof-of-Concept Intervention Study in Ambulatory Patients
Abstract
Introduction: The need for effective therapeutic regimens for non-critically ill patients during the COVID-19 pandemic remained largely unmet. Previous work has shown that a combination of three aromatic plants' essential oils (CAPeo) (Thymbra capitata (L.) Cav., Origanum dictamnus L., Salvia fruticose Mill.) has remarkable in vitro antiviral activity. Given its properties, it was urgent to explore its potential in treating mild COVID-19 patients in primary care settings.
Methods: A total of 69 adult patients were included in a clinical proof-of-concept (PoC) intervention study. Family physicians implemented the observational study in two arms (intervention group and control group) during three study periods (IG2020, n=13, IG2021/22, n=25, and CG2021/22, n=31). The SARS-CoV-2 infection was confirmed by real-time PCR. The CAPeo mixture was administered daily for 14 days per os in the intervention group, while the control group received usual care.
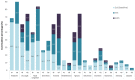
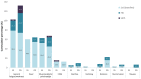
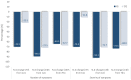
Results: The PoC study found that the number and frequency of general symptoms, including general fatigue, weakness, fever, and myalgia, decreased following CAPeo administration. By Day 7, the average presence (number) of symptoms decreased in comparison with Day 1 in IG (4.7 to 1.4) as well as in CG (4.0 to 3.1), representing a significant decrease in the cumulative presence in IC (-3.3 vs. -0.9, p < 0.001; η2 = 0.20) on Day 7 and on Day 14 (-4.2 vs. -2.9, p = 0.027; η2 = 0.08).
Discussion/conclusions: Our findings suggest that CAPeo possesses potent antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in addition tο its effect against influenza A and B and human rhinovirus HRV14 strains. The early and effective impact on alleviating key symptoms of COVID-19 may suggest this mixture can act as a complementary natural agent for patients with mild COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; effectiveness; essential oils; natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
Intellectual royalties (that are given to any inventor) are provided to CL, EC, and SAP. No commercial or other association exists with this Greek company.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Toxicity evaluation of an essential oil mixture from the Cretan herbs thyme, Greek sage and Cretan dittany.NPJ Sci Food. 2020 Nov 9;4(1):20. doi: 10.1038/s41538-020-00080-1. NPJ Sci Food. 2020. PMID: 33298942 Free PMC article.
-
Reconvalescent plasma/camostat mesylate in early SARS-CoV-2 Q-PCR positive high-risk individuals (RES-Q-HR): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2021 May 17;22(1):343. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05181-0. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34001215 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
The Therapeutic Potential of the Essential Oil of Thymbra capitata (L.) Cav., Origanum dictamnus L. and Salvia fruticosa Mill. And a Case of Plant-Based Pharmaceutical Development.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 24;11:522213. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.522213. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33390932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of green tea catechin, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCG) in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Major interactions with host/virus proteases.Phytomed Plus. 2023 Feb;3(1):100402. doi: 10.1016/j.phyplu.2022.100402. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Phytomed Plus. 2023. PMID: 36597465 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

