Antimicrobial efficacy of chlorine agents against selected oral pathogens
- PMID: 37606720
- PMCID: PMC10492701
- DOI: 10.1007/s00784-023-05190-0
Antimicrobial efficacy of chlorine agents against selected oral pathogens
Abstract
Objectives: Method-dependent comparison of antimicrobial agents' efficacy against oral pathogens.
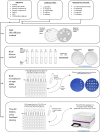
Materials and methods: Several sodium hypochlorite solutions (NaOCl)-Perisolv®, Carisolv® and Dakin's solution-were equated with chlorhexidine (CHX) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) against ten oral micro-organisms related to caries and periodontitis using different minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) techniques. Agents were adjusted to the final 70 mmol/L concentration of active chlorine molecule.
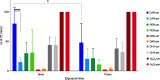
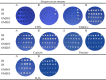
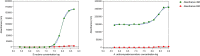
Results: Apart from H2O2 and the amino acids of Perisolv®, all the agents revealed an antimicrobial effect. Agar diffusion test ranked CHX (p < 0.05) as the most effective against all ten specimens, followed by the NaOCl of Perisolv® and Dakin's solution. Correspondingly, in broth microdilution on agar, CHX was the most effective in eradicating micro-organisms at 0.03 mmol/L compared with 2.2 mmol/L of Dakin's solution. In contrast, the bactericidal concentration of Dakin's solution was the most effective at 0.2 mmol/L, (p < 0.001), followed by Perisolv® (2.14 mmol/L), CHX (2.38 mmol/L) and Carisolv® (3.33 mmol/L) after 5 and 10 min in broth dilution test. In live/dead analysis, 60-min exposure to a 2-fold concentration of agents resulted in two-log Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans inhibition by CHX (35 mmol/L) whilst Streptococcus mutans was more susceptible, in 0.8 and 8.8 mmol/L, after 10 min to CHX and Dakin's respectively.
Conclusion: Replacement of CHX with tested hypochlorite agents showed evident potential and promoted rapid antimicrobial effect.
Clinical relevance: Effective antimicrobial agents are crucial in controlling pathogen-induced oral infections increasing clinical possibilities to combat oral biofilms. Additionally, CHX substitution with hypochlorite agents could eliminate CHX's adverse effects.
Keywords: Chlorhexidine; Chlorine compounds; Dakin’s; Dental caries; Oral disease; Periodontitis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Efficacy of taurine haloamines and chlorhexidine against selected oral microbiome species].Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 2013;65(3):187-96. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 2013. PMID: 24432558 Polish.
-
Tissue-dissolving capacity and antibacterial effect of buffered and unbuffered hypochlorite solutions.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002 Dec;94(6):756-62. doi: 10.1067/moe.2002.128961. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002. PMID: 12464903
-
Antiseptics Commonly Used in Total Joint Arthroplasty Interact and May Form Toxic Products.J Arthroplasty. 2018 Mar;33(3):844-846. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2017.10.028. Epub 2017 Nov 11. J Arthroplasty. 2018. PMID: 29137898
-
Influence of pH changes on chlorine-containing endodontic irrigating solutions.Int Endod J. 2011 Sep;44(9):792-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2011.01911.x. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Int Endod J. 2011. PMID: 21658076 Review.
-
Historical review of Dakin's solution applications.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018 Sep;71(9):e49-e55. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2018.05.023. Epub 2018 Jun 8. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018. PMID: 30173720 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Ocimum Tenuiflorum and Ocimum Gratissimum Herbal Formulation Against Oral Pathogens.Cureus. 2024 Feb 4;16(2):e53562. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53562. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38445144 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activity of Nanoformulated Chamomile and Green Tea-Based Mouthwash: An In Vitro Study.Cureus. 2024 Apr 2;16(4):e57470. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57470. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38699127 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

