Comparison of Ophthalmologist and Large Language Model Chatbot Responses to Online Patient Eye Care Questions
- PMID: 37606922
- PMCID: PMC10445188
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.30320
Comparison of Ophthalmologist and Large Language Model Chatbot Responses to Online Patient Eye Care Questions
Abstract
Importance: Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT appear capable of performing a variety of tasks, including answering patient eye care questions, but have not yet been evaluated in direct comparison with ophthalmologists. It remains unclear whether LLM-generated advice is accurate, appropriate, and safe for eye patients.
Objective: To evaluate the quality of ophthalmology advice generated by an LLM chatbot in comparison with ophthalmologist-written advice.
Design, setting, and participants: This cross-sectional study used deidentified data from an online medical forum, in which patient questions received responses written by American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO)-affiliated ophthalmologists. A masked panel of 8 board-certified ophthalmologists were asked to distinguish between answers generated by the ChatGPT chatbot and human answers. Posts were dated between 2007 and 2016; data were accessed January 2023 and analysis was performed between March and May 2023.
Main outcomes and measures: Identification of chatbot and human answers on a 4-point scale (likely or definitely artificial intelligence [AI] vs likely or definitely human) and evaluation of responses for presence of incorrect information, alignment with perceived consensus in the medical community, likelihood to cause harm, and extent of harm.
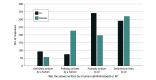
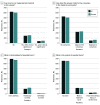
Results: A total of 200 pairs of user questions and answers by AAO-affiliated ophthalmologists were evaluated. The mean (SD) accuracy for distinguishing between AI and human responses was 61.3% (9.7%). Of 800 evaluations of chatbot-written answers, 168 answers (21.0%) were marked as human-written, while 517 of 800 human-written answers (64.6%) were marked as AI-written. Compared with human answers, chatbot answers were more frequently rated as probably or definitely written by AI (prevalence ratio [PR], 1.72; 95% CI, 1.52-1.93). The likelihood of chatbot answers containing incorrect or inappropriate material was comparable with human answers (PR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.77-1.10), and did not differ from human answers in terms of likelihood of harm (PR, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.67-1.07) nor extent of harm (PR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.80-1.22).
Conclusions and relevance: In this cross-sectional study of human-written and AI-generated responses to 200 eye care questions from an online advice forum, a chatbot appeared capable of responding to long user-written eye health posts and largely generated appropriate responses that did not differ significantly from ophthalmologist-written responses in terms of incorrect information, likelihood of harm, extent of harm, or deviation from ophthalmologist community standards. Additional research is needed to assess patient attitudes toward LLM-augmented ophthalmologists vs fully autonomous AI content generation, to evaluate clarity and acceptability of LLM-generated answers from the patient perspective, to test the performance of LLMs in a greater variety of clinical contexts, and to determine an optimal manner of utilizing LLMs that is ethical and minimizes harm.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Devlin J, Chang MW, Lee K, Toutanova K. BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv. Published online May 24, 2019. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1810.04805 - DOI
-
- Brown TB, Mann B, Ryder N, et al. Language models are few-shot learners. arXiv. Published online July 22, 2020. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2005.14165 - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

