Inhibition of VCP modulates NF-κB signaling pathway to suppress multiple myeloma cell proliferation and osteoclast differentiation
- PMID: 37606987
- PMCID: PMC10497005
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204965
Inhibition of VCP modulates NF-κB signaling pathway to suppress multiple myeloma cell proliferation and osteoclast differentiation
Abstract
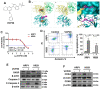
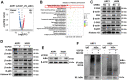
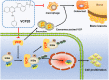
Multiple myeloma (MM) is the second most common hematological malignancy, in which the dysfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is associated with the pathogenesis. The valosin containing protein (VCP)/p97, a member of the AAA+ ATPase family, possesses multiple functions to regulate the protein quality control including ubiquitin-proteasome system and molecular chaperone. VCP is involved in the occurrence and development of various tumors while still elusive in MM. VCP inhibitors have gradually shown great potential for cancer treatment. This study aims to identify if VCP is a therapeutic target in MM and confirm the effect of a novel inhibitor of VCP (VCP20) on MM. We found that VCP was elevated in MM patients and correlated with shorter survival in clinical TT2 cohort. Silencing VCP using siRNA resulted in decreased MM cell proliferation via NF-κB signaling pathway. VCP20 evidently inhibited MM cell proliferation and osteoclast differentiation. Moreover, exosomes containing VCP derived from MM cells partially alleviated the inhibitory effect of VCP20 on cell proliferation and osteoclast differentiation. Mechanism study revealed that VCP20 inactivated the NF-κB signaling pathway by inhibiting ubiquitination degradation of IκBα. Furthermore, VCP20 suppressed MM cell proliferation, prolonged the survival of MM model mice and improved bone destruction in vivo. Collectively, our findings suggest that VCP is a novel target in MM progression. Targeting VCP with VCP20 suppresses malignancy progression of MM via inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: NF-κB; VCP; multiple myeloma; osteoclast differentiation; ubiquitination.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

