Hybrid Vesicles Enable Mechano-Responsive Hydrogel Degradation
- PMID: 37607024
- PMCID: PMC10600738
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202308509
Hybrid Vesicles Enable Mechano-Responsive Hydrogel Degradation
Abstract
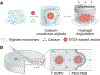
Stimuli-responsive hydrogels are intriguing biomimetic materials. Previous efforts to develop mechano-responsive hydrogels have mostly relied on chemical modifications of the hydrogel structures. Here, we present a simple, generalizable strategy that confers mechano-responsive behavior on hydrogels. Our approach involves embedding hybrid vesicles, composed of phospholipids and amphiphilic block copolymers, within the hydrogel matrix to act as signal transducers. Under mechanical stress, these vesicles undergo deformation and rupture, releasing encapsulated compounds that can control the hydrogel network. To demonstrate this concept, we embedded vesicles containing ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid (EGTA), a calcium chelator, into a calcium-crosslinked alginate hydrogel. When compressed, the released EGTA sequesters calcium ions and degrades the hydrogel. This study provides a novel method for engineering mechano-responsive hydrogels that may be useful in various biomedical applications.
Keywords: Block Copolymers; Functional Material; Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogel; Stress-Induced Degradation; Vesicles.
© 2023 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Figures




References
-
- Abalymov A, Van Der Meeren L, Saveleva M, Prikhozhdenko E, Dewettinck K, Parakhonskiy B, Skirtach AG, ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2020, 6, 3933–3944. - PubMed
-
- Yu P, Li Y, Sun H, Ke X, Xing J, Zhao Y, Xu X, Qin M, Xie J, Li J, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2022, 14, 27360–27370. - PubMed
-
- Lavrentieva A, Pepelanova I, Seliktar D, Tunable Hydrogels: Smart Materials for Biomedical Applications, Springer Nature, 2021. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

