Transcription factor 3 promotes migration and invasion potential and maintains cancer stemness by activating ID1 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 37607071
- PMCID: PMC10443991
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2023.2246206
Transcription factor 3 promotes migration and invasion potential and maintains cancer stemness by activating ID1 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
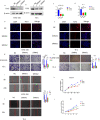
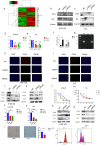
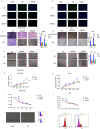
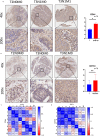
Transcription factor 3 (TCF3) is a member of the basic Helix - Loop - Helix (bHLH) transcription factor (TF) family and is encoded by the TCF3 gene (also known as E2A). It has been shown that TCF3 functions as a key transcription factor in the pathogenesis of several human cancers and plays an important role in stem cell maintenance and carcinogenesis. However, the effect of TCF3 in the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is poorly known. In our study, TCF3 was found to express highly and correlated with cancer stage and prognosis. TCF3 was shown to promote ESCC invasion, migration, and drug resistance both from the results of in vivo and in vitro assays. Moreover, further studies suggested that TCF3 played these roles through transcriptionally regulating Inhibitor of DNA binding 1(ID1). Notably, we also found that TCF3 or ID1 was associated with ESCC stemness. Furthermore, TCF3 was correlated with the expression of cancer stemness markers CD44 and CD133. Therefore, maintaining cancer stemness might be the underlying mechanism that TCF3 transcriptionally regulated ID1 and further promoted ESCC progression and drug resistance.
Keywords: ID1; TCF3; cancer stem cell; cancer stemness; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deubiquitinase USP8 increases ID1 stability and promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis.Cancer Lett. 2022 Aug 28;542:215760. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215760. Epub 2022 May 27. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35636624
-
SET domain-containing 5 is a potential prognostic biomarker that promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma stemness.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Apr 1;389(1):111861. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111861. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 31981592
-
Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 induces proliferation, migration, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and stemness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via post-transcriptional regulation of BMI1 and CTNNB1.Mol Oncol. 2020 Sep;14(9):2332-2351. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12683. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32239639 Free PMC article.
-
Circ-ATIC Serves as a Sponge of miR-326 to Accelerate Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Targeting ID1.Biochem Genet. 2022 Oct;60(5):1585-1600. doi: 10.1007/s10528-021-10167-3. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Biochem Genet. 2022. PMID: 35064360
-
The roles of the SOX2 protein in the development of esophagus and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and pharmacological target for therapy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jul;163:114764. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114764. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37100016 Review.
Cited by
-
The Predictive Value of BUB1 in the Prognosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int Dent J. 2025 Apr;75(2):1165-1175. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2024.07.012. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 39147662 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor TCF3 promotes bladder cancer development via TMBIM6-Ca2+-dependent ferroptosis.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Jul 3;11(1):303. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02585-8. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40610429 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
