Association of the time of day of EVT with clinical outcomes and benefit from successful recanalization after stroke
- PMID: 37607113
- PMCID: PMC10578882
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51877
Association of the time of day of EVT with clinical outcomes and benefit from successful recanalization after stroke
Abstract
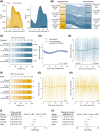
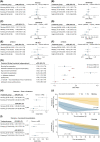
Experimental and neuroimaging studies suggest an influence of the time of day on acute infarct growth, but whether this could inform patient selection for acute treatments is uncertain. In a multicenter cohort of 9357 stroke patients undergoing endovascular treatment, morning treatment (05:00-10:59) was associated with lowest 90-day mRS scores (adjusted odds ratio, 1.27 [95% CI, 1.08-1.47]; p = 0.004). The association between successful recanalization and outcome was stronger in morning compared to evening-treated patients (pia = 0.046) with treatment benefit persisting until 24 h for morning-treated compared to 11.5 h for evening-treated patients suggesting that the time of day might inform patient selection for EVT.
© 2023 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
T. L. consults for Stryker Neurovascular GmbH and has received speaker honoraria from Pfizer, Covidien, Phenox, and Microvention, outside of this study. L. K. has received funding for travel or speaker honoraria from Bayer Vital, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol‐Meyer‐Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, and Pfizer, outside of this study, and funding for research from Boehringer Ingelheim. J. L. S. reports personal fees outside the submitted work from Phillips, Biogen, BrainsGate, Medtronic, and Rapid Medical. S. T. reports personal fees outside the submitted work from Apollo Alpha. The other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Beker MC, Caglayan B, Yalcin E, et al. Time‐of‐day dependent neuronal injury after ischemic stroke: implication of circadian clock transcriptional factor Bmal1 and survival kinase AKT. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(3):2565‐2576. - PubMed
-
- Tiedt S, Buchan AM, Dichgans M, Lizasoain I, Moro MA, Lo EH. The neurovascular unit and systemic biology in stroke ‐ implications for translation and treatment. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022;18(10):597‐612. - PubMed
-
- Rabinovich‐Nikitin I, Lieberman B, Martino TA, Kirshenbaum LA. Circadian‐regulated cell death in cardiovascular diseases. Circulation. 2019;139(7):965‐980. - PubMed
-
- Reidler P, Brehm A, Sporns PB, et al. Circadian rhythm of ischaemic core progression in human stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2021;94:70‐73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

