Metaproteogenomic Profile of a Mesopelagic Adenylylsulfate Reductase: Course-Based Discovery Using the Ocean Protein Portal
- PMID: 37607408
- PMCID: PMC10476264
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00152
Metaproteogenomic Profile of a Mesopelagic Adenylylsulfate Reductase: Course-Based Discovery Using the Ocean Protein Portal
Abstract
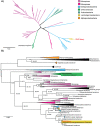
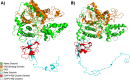
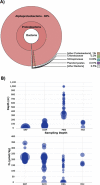
Adenylylsulfate reductase (Apr) is a flavoprotein with a dissimilatory sulfate reductase function. Its ability to catalyze the reverse reaction in sulfur oxidizers has propelled a complex phylogenetic history of transfers with sulfate reducers and made this enzyme an important protein in ocean sulfur cycling. As part of a graduate course, we analyzed metaproteomic data from the Ocean Protein Portal and observed evidence of Apr alpha (AprA) and beta (AprB) subunits in the Central Pacific Ocean. The protein was originally taxonomically attributed toChlorobium tepidum TLS, a green sulfur bacterium. However, our phylogenomic and oceanographic contextual analysis contradicted this label, instead showing that this protein is consistent with the genomic material from the newly discovered Candidatus Lambdaproteobacteriaclass, implying that the ecological role of this lineage in oxygen minimum twilight zones is underappreciated. This study illustrates how metaproteogenomic analysis can contribute to more accurate metagenomic/proteomic annotations and comprehensive ocean biogeochemical processes conducive to course-based research experiences.
Keywords: biogeochemistry; course-based research; metaproteogenomics; ocean metaproteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wójcik-Augustyn A.; Johansson A. J.; Borowski T. Reaction Mechanism Catalyzed by the Dissimilatory Adenosine 5′-Phosphosulfate Reductase. Adenosine 5′-Monophosphate Inhibitor and Key Role of Arginine 317 in Switching the Course of Catalysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Bioenerg. 2021, 1862, 148333. 10.1016/j.bbabio.2020.148333. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hu X.; Liu J.; Liu H.; Zhuang G.; Xun L. Sulfur Metabolism by Marine Heterotrophic Bacteria Involved in Sulfur Cycling in the Ocean. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 1369–1378. 10.1007/s11430-017-9234-x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

