Promotion of squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis by oncogene-mediated THG-1/TSC22D4 phosphorylation
- PMID: 37607779
- PMCID: PMC10551599
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.15934
Promotion of squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis by oncogene-mediated THG-1/TSC22D4 phosphorylation
Abstract
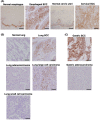
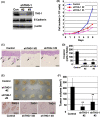
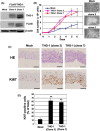
Carcinoma cells possess high proliferative and invasive potentials and exhibit a resilience against stresses, metabolic disorder, and therapeutic efforts. These properties are mainly acquired by genetic alterations including driver gene mutations. However, the detailed molecular mechanisms have not been fully elucidated. Here, we provide a novel mechanism connecting oncogenic signaling and the tumorigenic properties by a transforming growth factor-β1-stimulated clone 22 (TSC-22) family protein, THG-1 (also called as TSC22D4). THG-1 is localized at the basal layer of normal squamous epithelium and overexpressed in squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs). THG-1 knockdown suppressed SCC cell proliferation, invasiveness, and xenograft tumor formation. In contrast, THG-1 overexpression promoted the EGF-induced proliferation and stratified epithelium formation. Furthermore, THG-1 is phosphorylated by the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-RAS-ERK pathway, which promoted the oncogene-mediated tumorigenesis. Moreover, THG-1 involves in the alternative splicing of CD44 variants, a regulator of invasiveness, stemness, and oxidative stress resistance under the RTK pathway. These findings highlight the pivotal roles of THG-1 as a novel effector of SCC tumorigenesis, and the detection of THG-1 phosphorylation by our established specific antibody could contribute to cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Keywords: CD44; THG-1; TSC22D4; monoclonal antibody; phosphorylation; receptor tyrosine kinase; squamous cell carcinoma.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest. Dr. Mitsuyasu Kato is an associate editor of
Figures




References
-
- Alam M, Ratner D. Cutaneous squamous‐cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:975‐983. - PubMed
-
- Rustgi AK, El‐Serag HB. Esophageal carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2499‐2509. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Loos AH, McCarron P, et al. Trends in cervical squamous cell carcinoma incidence in 13 European countries: changing risk and the effects of screening. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005;14:677‐686. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

