Duplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for simultaneous detection of human and human male DNA
- PMID: 37608397
- PMCID: PMC10464483
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-023-06464-2
Duplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for simultaneous detection of human and human male DNA
Abstract
Objective: Screening of human and human male DNA is necessary for forensic DNA analyses. Although quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) is commonly used for detecting and quantifying these DNA targets, its use as a screening tool is time-consuming and labor-intensive. To streamline and simplify the screening process, we aimed to develop a duplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay capable of simultaneously detecting human and human male DNA in a single tube. We assessed the duplex LAMP assay for forensic application.
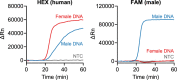
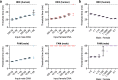
Results: For our duplex LAMP assay, we have utilized two fluorescent probes with HEX and FAM fluorophores to specifically detect human and human male DNA, respectively. The HEX (human target) signal was detected from both the male and female DNA samples, and the FAM (male target) signal was detected from only the male DNA sample. This assay has a sensitivity of 10-1 pg of DNA for both targets. Additionally, we successfully detected the two targets in the DNA samples extracted from forensically relevant body fluids, including blood, saliva, semen, and vaginal secretions.
Keywords: Duplex assay; Human DNA; Human male DNA; Loop-mediated isothermal amplification.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Nakahara H, Mizuno N, Fujii K, Sekiguchi K. Human DNA specific detection from forensic biological samples. Rep Natl Res Inst Polic Sci. 2007;58:66–74.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

