Progress in understanding and treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: recent insights and emerging therapies
- PMID: 37608885
- PMCID: PMC10440605
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1205948
Progress in understanding and treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: recent insights and emerging therapies
Abstract
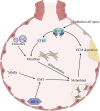
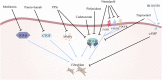
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a long-lasting, continuously advancing, and irrevocable interstitial lung disorder with an obscure origin and inadequately comprehended pathological mechanisms. Despite the intricate and uncharted causes and pathways of IPF, the scholarly consensus upholds that the transformation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts-instigated by injury to the alveolar epithelial cells-and the disproportionate accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, such as collagen, are integral to IPF's progression. The introduction of two novel anti-fibrotic medications, pirfenidone and nintedanib, have exhibited efficacy in decelerating the ongoing degradation of lung function, lessening hospitalization risk, and postponing exacerbations among IPF patients. Nonetheless, these pharmacological interventions do not present a definitive solution to IPF, positioning lung transplantation as the solitary potential curative measure in contemporary medical practice. A host of innovative therapeutic strategies are presently under rigorous scrutiny. This comprehensive review encapsulates the recent advancements in IPF research, spanning from diagnosis and etiology to pathological mechanisms, and introduces a discussion on nascent therapeutic methodologies currently in the pipeline.
Keywords: etiology; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; pathogenesis; progress; treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Guo, Sun, Zhang, Nie, Zhou and Zeng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

