Efficacy and safety of Tripterygium wilfordii multiglucoside for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a systematic review with bayesian meta-analysis
- PMID: 37608889
- PMCID: PMC10442163
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1183499
Efficacy and safety of Tripterygium wilfordii multiglucoside for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a systematic review with bayesian meta-analysis
Abstract
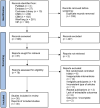
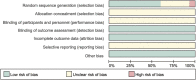
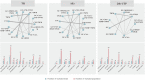
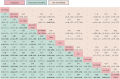
Background: Currently, the optimal therapy plan for idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN) remains controversial as there has been no comprehensive and systematic comparison of therapy plans for IMN. Therefore, in this study, a Bayesian meta-analysis was used to systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of various intervention plans involving traditional Chinese medicine TWM in the treatment of IMN. Methods: An electronic search in 7 databases was conducted from their inception to August 2022 for all published randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of various intervention plans for IMN. Network meta-analysis (NMA) was performed by using software R, and the surface under the cumulative ranking area (SUCRA) probability curve was plotted for each outcome indicator to rank the efficacy and safety of different intervention plans. Results: A total of 30 RCTs were included, involving 13 interventions. The results showed that (1) in terms of total remission (TR), ① GC + CNI + TWM was the best effective among all plans, and the addition and subtraction plan of CNI + TWM was the best effective for IMN; ② All plans involving TWM were more effective than GG; ③ Among monotherapy plans for IMN, TWM was more effective distinctly than GC, while TWM and CNI were similarly effective; ④ Among multidrug therapy plans for IMN, the addition of TWM to previously established therapy plans made the original plans more effective; ⑤The efficacy of combining TWM with other plans was superior to that of TWM alone. (2) In terms of lowering 24 h-UTP, GC + TWM was the best effective and more effective than TWM. (3) In terms of safety, there was no statistically significant difference between all groups. However, CNI + TWM was the safest. No serious adverse events (AEs) occurred in all the included studies. Conclusion: The addition of TWM may be beneficial to patients with IMN. It may enhance the efficacy of previously established treatment protocols without leading to additional safety risks. In particular, GC + CNI + TWM, GC + TWM, and CNI + TWM with better efficacy and higher safety can be preferred in clinical decision-making as the therapy plans for IMN.
Keywords: Tripterygium wilfordii Hook.f. (Celastraceae); adverse effects; immunosuppression; membranous nephropathy; network meta-analysis.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Liu, Xue, Wang and Yuan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tripterygium wilfordii multiglycosides combined with prednisone in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jan;99(5):e18970. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018970. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32000425 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of 12 immunosuppressive agents for idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults: A pairwise and network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 25;13:917532. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.917532. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35959430 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 31;10(7):e28836. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28836. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38596093 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective analysis of tacrolimus combined with Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycoside for treating idiopathic membranous nephropathy.BMC Nephrol. 2018 Jul 18;19(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-0967-5. BMC Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30021637 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicines combined with biomedicine in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 30;15:1391675. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1391675. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39539621 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Modified Huangqi Chifeng decoction alleviates podocyte injury on rat with experimental membranous nephropathy.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2459896. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2459896. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 39972601 Free PMC article.
-
IgG4-related disease complicated by PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy: A case report.Open Life Sci. 2024 Jul 25;19(1):20220921. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0921. eCollection 2024. Open Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39071497 Free PMC article.
-
Telitacicept monotherapy for refractory idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a case report and literature review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 8;12:1571616. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1571616. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40265191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ai L. M., Wang S. (2022). Study on the efficacy of tripterygium glycosides combined with low-dose hormone in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Shaanxi J. Traditional Chin. Med. 43 (06), 712–714.
-
- Bao J. B. (2020). Analysis of the efficacy of tripterygium glycosides and prednisone tablets in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J. Med. Inf. 33 (14), 157–158.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

