Therapeutic efficacy of tylvalosin combined with Poria cocos polysaccharides against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome
- PMID: 37609059
- PMCID: PMC10440737
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1242146
Therapeutic efficacy of tylvalosin combined with Poria cocos polysaccharides against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome
Abstract
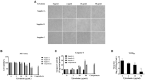
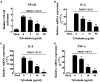
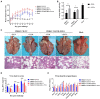
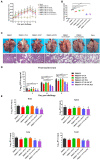
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) is one of the most economically important infectious diseases of pigs worldwide. Vaccination and various management measures have been implemented to control PRRS. However, due to high genetic diversity and insufficient understanding of the pathogenesis and immunological mechanisms, PRRS is still a challenge to the pig industry. Therefore, it is important to develop novel strategies to combat PRRS virus (PRRSV) infection. In this study, our data show that tylvalosin, a third-generation animal-specific macrolide, could inhibit PRRSV replication in MARC-145 cells, and suppress the PRRSV-induced NF-κB activation and cytokines expression. The pig infection experiment further demonstrated that tylvalosin could significantly reduce the virus loads in serum and tissues, and alleviate lung lesions of pigs infected with highly pathogenic PRRSV strains. The fever and loss of daily gain (LoDG) of the pigs were decreased as well. Considering the feature of immune suppression of PRRSV, a combination of tylvalosin with the immunopotentiator Poria cocos polysaccharides (PCP) was developed. Pig experiment showed this combination had a better therapeutic efficacy against PRRSV infection than tylvalosin and PCP alone in attenuating lung lesions, alleviating fever, and suppressing cytokines production. This study suggests that tylvalosin has significant antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects against PRRSV infection, and the combination of tylvalosin and PCP provides a promising strategy for PRRS treatment.
Keywords: NF-κB; Poria cocos polysaccharides (PCP); antiviral; cytokines; pig; porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS); tylvalosin.
Copyright © 2023 Shi, Luo, Wang, Dai, Chen, Li, Liu, Zhang, Huang and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of a water-soluble formulation of tylvalosin on disease caused by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus alone in sows or in combination with Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in piglets.BMC Vet Res. 2023 Feb 1;19(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12917-023-03571-x. BMC Vet Res. 2023. PMID: 36726139 Free PMC article.
-
Tylvalosin tartrate inhibits the replication stage of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus life cycle.Microb Pathog. 2024 Nov;196:106988. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106988. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39374883
-
Breaking the PRRSV-2 Life Cycle in Porcine Alveolar Macrophages: Tylvalosin's Multi-Stage Inhibition.Vet Sci. 2025 Apr 9;12(4):348. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12040348. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40284850 Free PMC article.
-
Live porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus vaccines: Current status and future direction.Vaccine. 2015 Aug 7;33(33):4069-80. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.06.092. Epub 2015 Jul 4. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26148878 Review.
-
Research Progress in Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus-Host Protein Interactions.Animals (Basel). 2022 May 27;12(11):1381. doi: 10.3390/ani12111381. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-omics profiling reveals Poria cocos polysaccharides mitigate PEDV-induced intestinal injury by modulating lipid metabolism in piglets.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025 May 20;16(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s40104-025-01211-y. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40390020 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation and transformation of tylvalosin by newly selected Providencia vermicola strain CT1: removal efficiency, pathways, mechanisms, and actual applications.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2025 May;48(5):749-760. doi: 10.1007/s00449-025-03140-6. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2025. PMID: 40074936
-
Baicalein inhibits PRRSV through direct binding, targeting EGFR, and enhancing immune response.Vet Res. 2025 Jan 20;56(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01440-5. Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 39833939 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated microbiome and metabolome analysis reveals that new insight into Radix pseudostellariae polysaccharide enhances PRRSV inactivated vaccine.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 26;15:1352018. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1352018. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38989282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keffaber KK. Reproductive failure of unknown etiology. Am Assoc Swine Pract News. (1989) 1:1–9.
-
- Holtkamp DJ, Kliebenstein JB, Neumann EJ, Zimmerman JJ, Rotto HF, Yoder TK, et al. . Assessment of the economic impact of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus on United States pork producers. J Swine Health Prod. (2013) 21:72–84. doi: 10.2460/javma.2005.227.385 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

