Rewarding outcomes enhance attentional capture and delay attentional disengagement
- PMID: 37609441
- PMCID: PMC10441522
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15868
Rewarding outcomes enhance attentional capture and delay attentional disengagement
Abstract
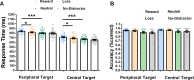
Attentional capture and disengagement are distinct process involved in attentional orienting. Most current studies have examined either the process of attentional capture or disengagement by manipulating stimuli associated with either positive (gains) or negative outcomes (losses). However, few studies have investigated whether attentional capture and disengagement are modulated by reward and loss outcomes. In the current study, we want to examine whether positive or negative outcomes could modulate distinguishing process of attentional capture and disengagement. Here, we manipulated different colored singleton stimuli associated with reward or loss outcomes; these stimuli were either presented at the center of screen or at the peripheral location. The participants' task was to search the target and identify the orientation of line segment in target as quickly as possible. The results showed that people had difficulty disengaging from a central reward-distractor, in comparison to loss- and neutral-distractor when target was presented at peripheral location. Similarly, peripheral reward-distractor captured more attention than loss- and neutral-distractor when target was presented at the center of screen after central fixation disappeared. Through our discoveries, we can conclude that positive rewards can increase attentional capture and delay attentional disengagement in healthy people.
Keywords: Attentional capture; Attentional disengagement; Loss; Reward.
©2023 Yan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Working memory components modulation of attentional disengagement from evaluative distractor.Psych J. 2024 Oct;13(5):717-725. doi: 10.1002/pchj.748. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Psych J. 2024. PMID: 38530871 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluative distractors modulate attentional disengagement: People would rather stay longer on rewards.J Vis. 2022 Jul 11;22(8):12. doi: 10.1167/jov.22.8.12. J Vis. 2022. PMID: 35848902 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed disengagement of attention from distractors signalling reward.Cognition. 2020 Feb;195:104125. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2019.104125. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Cognition. 2020. PMID: 31751815
-
Attentional disengagement effect based on relevant features.Front Psychol. 2022 Nov 9;13:960183. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.960183. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36438363 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of gains and losses to attentional capture and disengagement: evidence from the gap paradigm.Exp Brain Res. 2021 Nov;239(11):3381-3395. doi: 10.1007/s00221-021-06210-9. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Exp Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 34495366
Cited by
-
Working memory components modulation of attentional disengagement from evaluative distractor.Psych J. 2024 Oct;13(5):717-725. doi: 10.1002/pchj.748. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Psych J. 2024. PMID: 38530871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albertella L, Le Pelley ME, Chamberlain SR, Westbrook F, Fontenelle LF, Segrave R, Lee R, Pearson D. Reward-related attentional capture is associated with severity of addictive and obsessive–compulsive behaviors. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors. 2019;33(5):495–502. doi: 10.1037/adb0000484.supp. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

