The Role of Self-Care Acupressure in Maternal Health Problems to Support the Sustainable Development Goals Program in the Health Sector: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 37609550
- PMCID: PMC10440639
- DOI: 10.1089/acu.2023.0001
The Role of Self-Care Acupressure in Maternal Health Problems to Support the Sustainable Development Goals Program in the Health Sector: A Narrative Review
Abstract
Objective: This narrative review discusses several studies that demonstrated the effect of self-care acupressure, especially on maternal-health problems in antenatal, labor, and postpartum times, as well as the mechanism of acupressure, the points used, and treatment strategies to support the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) program in the health sector.
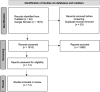
Methods: PubMed and Google Scholar were searched for randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews/meta-analyses from the date of their inception to February 2022.
Results: The 14 studies that were included showed the possibility that acupressure could have a positive impact on maternal health. This self-care can be the main alternative in overcoming the gap in solving health problems in the world.
Conclusions: Self-care acupressure at various acupoints has been shown to be feasible to reduce problems during antenatal, labor, and postpartum times. Additional research on the use of acupressure during pregnancy and cross-sectional collaboration to increase the awareness of acupressure techniques are needed.
Keywords: Sustainable Development Goals; acupressure; maternal health; self-care.
Copyright 2023, Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers.
Conflict of interest statement
No financial conflicts of interest exist.
References
-
- Wass V. The Astana declaration 2018. Educ Prim Care. 2018;29(6):321. - PubMed
-
- Guégan JF, Suzán G, Kati-Coulibaly S, et al. . Sustainable Development Goal #3, “health and well-being,” and the need for more integrative thinking. Veterinaria Mexico. 2018;5(2).1–18
-
- Johnston RB. Arsenic and the 2030 agenda for sustainable development: Arsenic research and global sustainability In: Proceedings of the 6th International Congress on Arsenic in the Environment, New York, September 25–27, 2015:12–14.
-
- World Health Organisation. Reproductive Health Strategy: To Accelerate Progress Towards the Attainment of International Development Goals and Targets. Department of Reproductive Health and Research, WHO, Geneva. 2004; Online document at: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/68754/WHO_RHR_04.8.pdf;... Accessed June 3, 2023. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Trends in Maternal Mortality: 2000 to 2017. Estimates by WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, World Bank Group and the United Nations Population Division: Executive Summary. Geneva: WHO; 2019.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous