Tuberculosis medicines for children in Europe: an unmet medical need
- PMID: 37609597
- PMCID: PMC10440650
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00730-2022
Tuberculosis medicines for children in Europe: an unmet medical need
Abstract
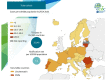
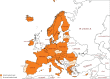
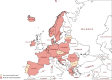
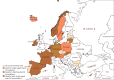
The availability of first-line medicines for the treatment of drug-susceptible tuberculosis (TB) is inconsistent across European countries. This is particularly worrisome for child-friendly medicines. There are reported examples of physicians being forced to adapt and/or combine formulations intended for adults to treat children with TB. Reduced compliance, unknown effects on treatment outcomes and unpredictable toxicity are potential consequences of resorting to these suboptimal treatment options. Furthermore, the use of these alternatives may increase the risk of drug-resistant TB. This study analysed the availability and use of TB medicines in the European Union (EU)/European Economic Area, with a particular focus on child-friendly formulations. We sought to carry out a full review of the situation by means of a survey involving the EU regulatory network. Countries were asked to confirm marketing status of anti-drug-susceptible-TB medicines, ways used to overcome their absence in their territory and the general difficulties they face to treat children with TB. Results confirmed that rifampicin suspension is the only child-friendly formulation available in Europe, approved in just 10 member states. Overall, 24 countries out of 30 considered the lack of adequate drug-susceptible TB medicines an unmet medical need. To overcome this, countries confirmed that they resort to importation or use adapted formulations. The joint forces of European institutions and pharmaceutical industry are crucial for the development of paediatric formulations and contribute to better compliance and health outcomes.
Copyright ©The authors 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) . WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis. Module 4: Treatment – Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis Treatment. 2022. www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240048126 Date last accessed: 1 July 2022. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization , European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control . Tuberculosis Surveillance and Monitoring in Europe 2022: 2020 Data. 2022. www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/Tuberculosis-surveillan... Date last accessed: 1 July 2022.
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control . Infographic: Tuberculosis in the EU/EEA 2020. 2022. www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/infographic-tuberculosis-eueea-2020 Date last accessed: 1 July 2022.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) .Tuberculosis Profile. 2022. https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/tb_profiles/?_inputs_&entity_type=%2.... Date last accessed: 24 July 2022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
