The T1D Index: Implications of Initial Results, Data Limitations, and Future Development
- PMID: 37610700
- PMCID: PMC10520097
- DOI: 10.1007/s11892-023-01520-4
The T1D Index: Implications of Initial Results, Data Limitations, and Future Development
Erratum in
-
Correction to: The T1D Index: Implications of Initial Results, Data Limitations, and Future Development.Curr Diab Rep. 2023 Oct;23(10):305. doi: 10.1007/s11892-023-01524-0. Curr Diab Rep. 2023. PMID: 37707770 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose of the review: Current global information on incidence, prevalence, and mortality of type 1 diabetes (T1D) is limited, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. To address this gap in evidence, JDRF, Life for a Child, International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes, and International Diabetes Federation have developed the T1D Index, which uses a Markov mathematical model, and machine learning and all available data to provide global estimates of the burden on T1D. This review assesses the methodology, limitations, current findings, and future directions of the Index.
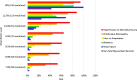
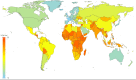
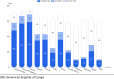
Recent findings: Global prevalence was estimated at 8.4 million in 2021, with 1.5 million <20 years (y). T1D prevalence varied from 1.5 to 534 per 100,000, with T1D accounting for <0.1-17.8% of all diabetes in different countries. A total of 35,000 young people <25 y are estimated to have died at clinical onset of T1D from non-diagnosis. An estimated 435,000 people <25 y were receiving "minimal care." Health-adjusted life years (HALYs) lost for individuals diagnosed with T1D at age 10 y in 2021 ranged from 14 to 55 y. These results show that interventions to reduce deaths from non-diagnosis, and improve access to at least an intermediate care level, are needed to reduce projected life years lost. The results have significant uncertainties due to incomplete data across the required inputs. Obtaining recent incidence, prevalence, and mortality data, as well as addressing data quality issues, misdiagnoses, and the lack of adult data, is essential for maintaining and improving accuracy. The index will be updated regularly as new data become available.
Keywords: Diabetes-related mortality; Epidemiology; Healthy life years; Incidence; Prevalence; Type 1 diabetes.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ogle GD, James S, Dabelea D, Pihoker C, Svennson J, Maniam J, et al. •Global estimates of incidence of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents: results from the International Diabetes Federation Atlas, 10th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109083. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109083. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tuomilehto J, Ogle GD, Lund-Blix NA, Stene LC. Update on worldwide trends in occurrence of childhood type 1 diabetes in 2020. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2020;17:198–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

