Sperm and northern bottlenose whale interactions with deep-water trawlers in the western North Atlantic
- PMID: 37610993
- PMCID: PMC10446179
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289626
Sperm and northern bottlenose whale interactions with deep-water trawlers in the western North Atlantic
Abstract
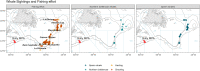
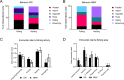
Commercial fisheries have increased in all the world's oceans with diverse unintended impacts on marine ecosystems. As a result of resource overlap, interactions between cetaceans and fisheries are a common occurrence and, in many cases, can give rise to significant conservation issues. Research on the distribution and types of such interactions is important for efficient management. In this study, we describe the behaviors of two whale species: sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus) and northern bottlenose whales (Hyperoodon ampullatus), interacting with benthic trawlers fishing off the eastern Grand Banks of the western North Atlantic in 2007. Whale interactions were only observed when vessels were targeting Greenland halibut (Reinhardtius hippoglossoides) in deep-water fishing areas and were most common during net hauling. Sperm whales and northern bottlenose whales appeared to engage in feeding behavior close to the surface during hauling, especially during the latter stages, suggesting they targeted fish escapees rather than discards. Using photo-identification methods, seven individual sperm whales were identified with multiple resights of six individuals being recorded over an almost two month period. The maximum distance between two resights was 234 km, suggesting individual sperm whales were repeatedly targeting and even following fishing vessels over multiple days and between fishing areas. By contrast, there were no photographic resights of individual northern bottlenose whales within this study, or with substantial photo-identification catalogues from other adjacent high density areas, suggesting that individuals of this species may be less likely to follow vessels or move between areas. This study documents the earliest confirmed records of northern bottlenose whales in this remote region. These interactions and high encounter rates may indicate that adjacent populations are recovering from the previous century of commercial whaling. Our study provides new insights and details on whale-fisheries interactions, which can inform future research and help managers understand the real and perceived impacts of depredation behaviour on fisheries and whales.
Copyright: © 2023 Oyarbide et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Crowder LB, Hazen EL, Avissar N, Bjorkland R, Latanich C, Ogburn MB. The Impacts of Fisheries on Marine Ecosystems and the Transition to Ecosystem-Based Management. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics. 2008;39:259–78.
-
- Jog K, Sutaria D, Diedrich A, Grech A, Marsh H. Marine Mammal Interactions With Fisheries: Review of Research and Management Trends Across Commercial and Small-Scale Fisheries. Frontiers in Marine Science. 2022;9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.758013 - DOI
-
- Read AJ. The Looming Crisis: Interactions between Marine Mammals and Fisheries. Journal of Mammalogy. 2008;89(3):541–8.
-
- Carlucci R, Capezzuto F, Cipriano G, D’Onghia G, Fanizza C, Libralato S, et al.. Assessment of cetacean–fishery interactions in the marine food web of the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central Mediterranean Sea). Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries. 2020;31(1):135–56. doi: 10.1007/s11160-020-09623-x - DOI
-
- Amelot M, Plard F, Guinet C, Arnould JPY, Gasco N, Tixier P. Increasing numbers of killer whale individuals use fisheries as feeding opportunities within subantarctic populations. Biol Lett. 2022;18(2):20210328. Epub 2022/02/02. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2021.0328 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8807058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

