Candida albicans stimulates formation of a multi-receptor complex that mediates epithelial cell invasion during oropharyngeal infection
- PMID: 37611070
- PMCID: PMC10479894
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011579
Candida albicans stimulates formation of a multi-receptor complex that mediates epithelial cell invasion during oropharyngeal infection
Abstract
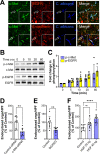
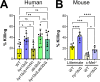
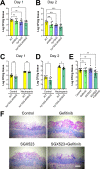
Fungal invasion of the oral epithelium is central to the pathogenesis of oropharyngeal candidiasis (OPC). Candida albicans invades the oral epithelium by receptor-induced endocytosis but this process is incompletely understood. We found that C. albicans infection of oral epithelial cells induces c-Met to form a multi-protein complex with E-cadherin and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). E-cadherin is necessary for C. albicans to activate both c-Met and EGFR and to induce the endocytosis of C. albicans. Proteomics analysis revealed that c-Met interacts with C. albicans Hyr1, Als3 and Ssa1. Both Hyr1 and Als3 are required for C. albicans to stimulate c-Met and EGFR in oral epithelial cells in vitro and for full virulence during OPC in mice. Treating mice with small molecule inhibitors of c-Met and EGFR ameliorates OPC, demonstrating the potential therapeutic efficacy of blocking these host receptors for C. albicans.
Copyright: © 2023 Phan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures







Update of
-
Candida albicans stimulates the formation of a multi-receptor complex that mediates epithelial cell invasion during oropharyngeal infection.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 23:2023.02.23.529756. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.23.529756. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2023 Aug 23;19(8):e1011579. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011579. PMID: 36865306 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Serrano J, Lopez-Pintor RM, Ramirez L, Fernandez-Castro M, Sanz M, Melchor S, et al. Risk factors related to oral candidiasis in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2020;25(5):e700–e5. Epub 2020/07/20. doi: 10.4317/medoral.23719 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC7473438. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saito H, Shodo R, Yamazaki K, Katsura K, Ueki Y, Nakano T, et al. The association between oral candidiasis and severity of chemoradiotherapy-induced dysphagia in head and neck cancer patients: A retrospective cohort study. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2020;20:13–8. Epub 2019/11/19. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2019.10.006 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6849117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guilbert TW, Colice G, Grigg J, van Aalderen W, Martin RJ, Israel E, et al. Real-life outcomes for patients with asthma prescribed spacers for use with either extrafine- or fine-particle inhaled corticosteroids. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017;5(4):1040–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2016.11.026 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

