Cell-type-specific regulation of APOE and CLU levels in human neurons by the Alzheimer's disease risk gene SORL1
- PMID: 37611586
- PMCID: PMC10568487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112994
Cell-type-specific regulation of APOE and CLU levels in human neurons by the Alzheimer's disease risk gene SORL1
Abstract
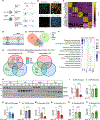
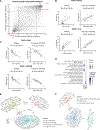
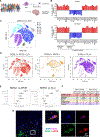
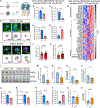
SORL1 is implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) through genetic studies. To interrogate the roles of SORL1 in human brain cells, SORL1-null induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) were differentiated to neuron, astrocyte, microglial, and endothelial cell fates. Loss of SORL1 leads to alterations in both overlapping and distinct pathways across cell types, with the greatest effects in neurons and astrocytes. SORL1 loss induces a neuron-specific reduction in apolipoprotein E (APOE) and clusterin (CLU) and altered lipid profiles. Analyses of iPSCs derived from a large cohort reveal a neuron-specific association between SORL1, APOE, and CLU levels, a finding validated in postmortem brain. Enhancement of retromer-mediated trafficking rescues tau phenotypes observed in SORL1-null neurons but does not rescue APOE levels. Pathway analyses implicate transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)/SMAD signaling in SORL1 function, and modulating SMAD signaling in neurons alters APOE RNA levels in a SORL1-dependent manner. Taken together, these data provide a mechanistic link between strong genetic risk factors for AD.
Keywords: APOE; Alzheimer's; CLU; CP: Neuroscience; SMAD; SORL1; TGFbeta; amyloid; endolysosomal; retromer; tau.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Cell-type-specific regulation of APOE levels in human neurons by the Alzheimer's disease risk gene SORL1.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 25:2023.02.25.530017. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.25.530017. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cell Rep. 2023 Aug 29;42(8):112994. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112994. PMID: 36865313 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Lambert JC, Ibrahim-Verbaas CA, Harold D, Naj AC, Sims R, Bellenguez C, DeStafano AL, Bis JC, Beecham GW, Grenier-Boley B, et al. (2013). Meta-Analysis of 74,046 Individuals Identifies 11 New Susceptibility Loci for Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Genet. 45, 1452–1458. 10.1038/ng.2802. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pottier C, Hannequin D, Coutant S, Rovelet-Lecrux A, Wallon D, Rousseau S, Legallic S, Paquet C, Bombois S, Pariente J, et al. ; PHRC GMAJ Collaborators (2012). High Frequency of Potentially Pathogenic SORL1 Mutations in Autosomal Dominant Early-Onset Alzheimer Disease. Mol. Psychiatr. 17, 875–879. 10.1038/mp.2012.15. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holstege H, van der Lee SJ, Hulsman M, Wong TH, van Rooij JG, Weiss M, Louwersheimer E, Wolters FJ, Amin N, Uitterlinden AG, et al. (2017). Characterization of Pathogenic SORL1 Genetic Variants for Association with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Clinical Interpretation Strategy. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 25, 973–981. 10.1038/ejhg.2017.87. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

