Regulated cell death pathways and their roles in homeostasis, infection, inflammation, and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 37612410
- PMCID: PMC10474065
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-023-01069-y
Regulated cell death pathways and their roles in homeostasis, infection, inflammation, and tumorigenesis
Abstract
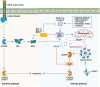
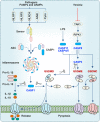
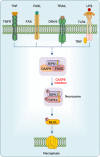
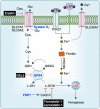
Pyroptosis, apoptosis, necroptosis, and ferroptosis, which are the most well-studied regulated cell death (RCD) pathways, contribute to the clearance of infected or potentially neoplastic cells, highlighting their importance in homeostasis, host defense against pathogens, cancer, and a wide range of other pathologies. Although these four RCD pathways employ distinct molecular and cellular processes, emerging genetic and biochemical studies have suggested remarkable flexibility and crosstalk among them. The crosstalk among pyroptosis, apoptosis and necroptosis pathways is more evident in cellular responses to infection, which has led to the conceptualization of PANoptosis. In this review, we provide a brief overview of the molecular mechanisms of pyroptosis, apoptosis, necroptosis, and ferroptosis and their importance in maintaining homeostasis. We discuss the intricate crosstalk among these RCD pathways and the current evidence supporting PANoptosis, focusing on infectious diseases and cancer. Understanding the fundamental processes of various cell death pathways is crucial to inform the development of new therapeutics against many diseases, including infection, sterile inflammation, and cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulated cell death in cancer: from pathogenesis to treatment.Chin Med J (Engl). 2023 Mar 20;136(6):653-665. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002239. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023. PMID: 35950752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From pyroptosis, apoptosis and necroptosis to PANoptosis: A mechanistic compendium of programmed cell death pathways.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Aug 3;19:4641-4657. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.07.038. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34504660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of inflammatory cell death-PANoptosis in health and disease.Arch Pharm Res. 2024 Jul;47(7):617-631. doi: 10.1007/s12272-024-01506-0. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Arch Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 38987410 Review.
-
Targeting cell death pathways for cancer therapy: recent developments in necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis research.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Dec 8;15(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01392-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36482419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modes of Regulated Cell Death in Cancer.Cancer Discov. 2021 Feb;11(2):245-265. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0789. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Cancer Discov. 2021. PMID: 33462123 Review.
Cited by
-
Apigenin: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential against Cancer Spreading.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 20;25(10):5569. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105569. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRIM56 Modulates YBX1 Degradation to Ameliorate ZBP1-Mediated Neuronal PANoptosis in Spinal Cord Injury.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Nov;11(42):e2407132. doi: 10.1002/advs.202407132. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39291396 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting cell death and tumor immunity in cancer therapy: challenges and future directions.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jun 3;12:1416115. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1416115. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38887519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of crucial inflammaging related risk factors in multiple sclerosis.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 May 21;17:1398665. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1398665. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38836117 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts in carcinogenesis.J Transl Med. 2025 Jan 13;23(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06071-8. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39806363 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

