Exploring the mechanism of luteolin by regulating microglia polarization based on network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- PMID: 37612462
- PMCID: PMC10447507
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-41101-9
Exploring the mechanism of luteolin by regulating microglia polarization based on network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
Abstract
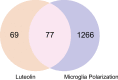
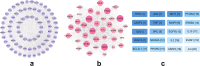
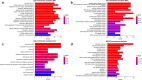
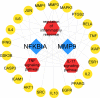
Neuroinflammation manifests following injury to the central nervous system (CNS) and M1/M2 polarization of microglia is closely associated with the development of this neuroinflammation. In this study, multiple databases were used to collect targets regarding luteolin and microglia polarization. After obtaining a common target, a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was created and further analysis was performed to obtain the core network. Molecular docking of the core network with luteolin after gene enrichment analysis. In vitro experiments were used to examine the polarization of microglia and the expression of related target proteins. A total of 77 common targets were obtained, and the core network obtained by further analysis contained 38 proteins. GO and KEGG analyses revealed that luteolin affects microglia polarization in regulation of inflammatory response as well as the interleukin (IL)-17 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathways. Through in vitro experiments, we confirmed that the use of luteolin reduced the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), IL-6, TNF-α, p-NFκBIA (p-IκB-α), p-NFκB p65, and MMP9, while upregulating the expression of Arg-1 and IL-10. This study reveals various potential mechanisms by which luteolin induces M2 polarization in microglia to inhibit the neuroinflammatory response.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oxymatrine inhibits neuroinflammation byRegulating M1/M2 polarization in N9 microglia through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Nov;100:108139. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108139. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34517275
-
The mechanism of Epimedium in the treatment of coronary atherosclerotic heart disease based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and in vitro studies.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Apr;26(7):2478-2488. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202204_28482. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35442463
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Luteolin Against Atopic Dermatitis Based on Network Pharmacology and in vivo Experimental Validation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Dec 9;16:4205-4221. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S387893. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 36530790 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin inhibits the JAK/STAT pathway to alleviate auditory cell apoptosis of acquired sensorineural hearing loss based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation, and experiments in vitro.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2024 Jan;482:116790. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2023.116790. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38103742
-
Role of corn silk for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: A mechanism research based on network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2023 Nov;102(5):1231-1247. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14315. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2023. PMID: 37563784
Cited by
-
Network pharmacology-based pharmacological mechanism prediction of Lycii Fructus against postmenopausal osteoporosis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 1;102(48):e36292. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036292. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38050297 Free PMC article.
-
Swertiamarin and sweroside are potential inhibitors of COVID-19 based on the silico analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 8;103(45):e40425. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040425. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39533611 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the anti-atherosclerosis mechanisms of Tanyu Tongzhi formula based on network pharmacology, Mendelian randomization, and experimental verification.Pharm Biol. 2024 Dec;62(1):790-802. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2415666. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Pharm Biol. 2024. PMID: 39450854 Free PMC article.
-
Yixin-Fumai granules modulate autophagy through the PI3K/AKT/FOXO pathway and lead to amelioration of aging mice with sick sinus syndrome.Immun Ageing. 2024 Jul 6;21(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12979-024-00439-y. Immun Ageing. 2024. PMID: 38971780 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoformulated herbal compounds: enhanced antibacterial efficacy of camphor and thymol-loaded nanogels.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Apr 2;24(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04435-z. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 38566054 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

