M6A-mediated-upregulation of lncRNA BLACAT3 promotes bladder cancer angiogenesis and hematogenous metastasis through YBX3 nuclear shuttling and enhancing NCF2 transcription
- PMID: 37612524
- PMCID: PMC10541332
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-023-02814-3
M6A-mediated-upregulation of lncRNA BLACAT3 promotes bladder cancer angiogenesis and hematogenous metastasis through YBX3 nuclear shuttling and enhancing NCF2 transcription
Erratum in
-
Correction: M6A-mediated-upregulation of lncRNA BLACAT3 promotes bladder cancer angiogenesis and hematogenous metastasis through YBX3 nuclear shuttling and enhancing NCF2 transcription.Oncogene. 2025 Oct;44(40):3879-3882. doi: 10.1038/s41388-025-03575-x. Oncogene. 2025. PMID: 40962859 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
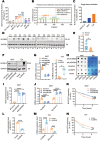
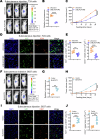
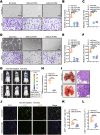
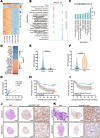
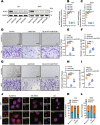
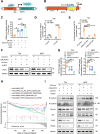
Lymphatic metastasis is recognized as the leading manner of metastasis in bladder cancer (BLCa), but hematogenous metastasis accounts for a majority of cancer-associated deaths. The past two decades have witnessed tremendous attention in long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), which are a new hope for the development of targeted drug therapy for metastatic cancers; however, the underlying mechanism of lncRNAs involved in BLCa hematogenous metastasis remains to be elucidated. Here, we identified BLCa-associated transcript 3 (BLACAT3), a lncRNA, which was aberrantly upregulated in BLCa and corelated with poor prognosis of patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Methodologically, m6A epitranscriptomic microarray, RNA sequencing and mass spectrometry (MS) were used to screen the key molecules of the regulatory axis. Functional assays, animal models and clinical samples were used to explore the roles of BLACAT3 in BLCa in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, m6A modification contributes to BLACAT3 upregulation by stabilizing RNA structure. BLACAT3 recruits YBX3 to shuttle into the nucleus, synergistically enhances NCF2 transcription, and promotes BLCa angiogenesis and hematogenous metastasis by activating downstream NF-κB signaling. Our findings will develop prognosis prediction tools for BLCa patients and discover novel therapeutic biological targets for metastatic BLCa.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Compérat E, Amin MB, Cathomas R, Choudhury A, De Santis M, Kamat A, et al. Current best practice for bladder cancer: a narrative review of diagnostics and treatments. Lancet (Lond, Engl). 2022;400:1712–21. - PubMed
-
- Babjuk M, Burger M, Zigeuner R, Shariat SF, van Rhijn BW, Compérat E, et al. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2013. Eur Urol. 2013;64:639–53. - PubMed
-
- Witjes JA, Bruins HM, Cathomas R, Compérat EM, Cowan NC, Gakis G, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Summary of the 2020 Guidelines. Eur Urol. 2021;79:82–104. - PubMed
-
- Kamat AM, Hahn NM, Efstathiou JA, Lerner SP, Malmström PU, Choi W, et al. Bladder cancer. Lancet (Lond, Engl). 2016;388:2796–810. - PubMed
-
- Raby SEM, Hoskin P, Choudhury A. The role of palliative radiotherapy in bladder cancer: a narrative review. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9:4294–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

