Prognostic value of translationally controlled tumor protein in colon cancer
- PMID: 37614375
- PMCID: PMC10442730
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2023.2668
Prognostic value of translationally controlled tumor protein in colon cancer
Abstract
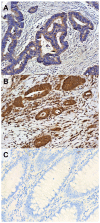
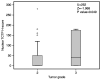
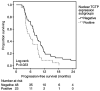
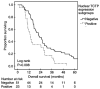
The translationally controlled tumor protein (TCTP) is a highly conserved protein involved in a variety of normal cell functions and disease processes. Preclinical studies revealed that TCTP has anti-apoptotic properties, promotes cell growth and division and is involved in cancer progression by promoting invasion and metastasis. The present study explored the potential value of TCTP as a prognostic marker in colon cancer. A retrospective analysis of 74 patients with colon cancer was performed. Using immunohistochemistry, TCTP levels in the primary tumor were assessed semi-quantitatively by the calculation of cytoplasmic and nuclear H-score. Cytoplasmic TCTP levels in the primary tumor had no statistically significant association with disease-free survival (DFS), progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the present patient population. Patients whose primary tumors had a negative nuclear TCTP expression had significantly improved clinical outcomes. The PFS for the negative nuclear TCTP expression group was 7.7 months [95% confidence interval (CI), 5.8-9.5] compared with 5.5 months (95% CI, 3.2-7.8) in the group with positive nuclear expression (P=0.023, Mantel-Cox log-rank). Patients with a negative nuclear expression of TCTP had a significantly higher median OS (22.2 months; 95% CI, 16.1-28.3) compared with those with positive TCTP nuclear expression (median 13.2 months; 95% CI, 10.1-16.3; P=0.008, Mantel-Cox log-rank). In a multivariate Cox regression model, a positive nuclear TCTP H-score was an independent risk factor for worse PFS and OS. The 1-year OS rate in the group with negative nuclear TCTP expression was 86.3% compared with 56.5% in patients with positive nuclear TCTP expression (P=0.008). The present study suggested that semiquantitative H-score measurement of TCTP levels in the nuclei of tumor cells from the primary tumor is a potential prognostic marker for clinical outcomes in patients with colon cancer.
Keywords: colon cancer; prognostic marker; survival; translationally controlled tumor protein.
Copyright: © Stoyanov et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
