A fuzzy decision support model for the evaluation and selection of healthcare projects in the framework of competition
- PMID: 37614458
- PMCID: PMC10442559
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1222125
A fuzzy decision support model for the evaluation and selection of healthcare projects in the framework of competition
Abstract
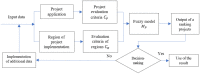
Our research aims to support decision-making regarding the financing of healthcare projects by structural funds with policies targeting reduction of the development gap among different regions and countries of the European Union as well as the achievement of economic and social cohesion. A fuzzy decision support model for the evaluation and selection of healthcare projects should rank the project applications for the selected region, accounting for the investor's wishes in the form of a regional coefficient in order to reduce the development gap between regions. On the one hand, our proposed model evaluates project applications based on selected criteria, which may be structured, weakly structured, or unstructured. On the other hand, it also incorporates information on the level of healthcare development in the region. The obtained ranking increases the degree of validity of the decision regarding the selection of projects for financing by investors, considering the level of development of the region where the project will be implemented. At the expense of European Union (EU) structural funds, a village, city, region, or state can receive funds for modernization and development of the healthcare sector and all related processes. To minimize risks, it is necessary to implement adequate support systems for decision-making in the assessment of project applications, as well as regional policy in the region where the project will be implemented. The primary goal of this study was to develop a complex fuzzy decision support model for the evaluation and selection of projects in the field of healthcare with the aim of reducing the development gap between regions. Based on the above description, we formed the following scientific hypothesis for this research: if the project selected for financing can successfully achieve its stated goals and increase the level of development of its region, it should be evaluated positively. This evaluation can be obtained using a complex fuzzy model constructed to account for the region's level of development in terms of the availability and quality of healthcare services in the region where the project will be implemented.
Keywords: European Green Deal; decision-making; expert evaluation; fuzzy sets; healthy cities; industry 5.0; projects.
Copyright © 2023 Gavurova, Kelemen, Polishchuk, Mudarri and Smolanka.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous