Experts' Perceived Patient Burden and Outcomes of Knee-ankle-foot-orthoses (Kafos) Vs. Microprocessor-stance-and-swing-phase-controlled-knee-ankle-foot Orthoses (Mp-sscos)
- PMID: 37614478
- PMCID: PMC10443469
- DOI: 10.33137/cpoj.v5i1.37795
Experts' Perceived Patient Burden and Outcomes of Knee-ankle-foot-orthoses (Kafos) Vs. Microprocessor-stance-and-swing-phase-controlled-knee-ankle-foot Orthoses (Mp-sscos)
Abstract
Background: Patients with neuromuscular knee-instability assisted with orthotic devices experience problems including pain, falls, mobility issues and limited engagement in daily activities.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to analyse current real-life burden, needs and orthotic device outcomes in patients in need for advanced orthotic knee-ankle-foot-orthoses (KAFOs).
Methodology: An observer-based semi-structured telephone interview with orthotic care experts in Germany was applied. Interviews were transcribed and content-analysed. Quantitative questions were analysed descriptively.
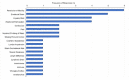
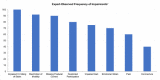
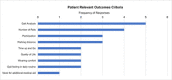
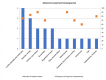
Findings: Clinical experts from eight centres which delivered an average of 49.9 KAFOs per year and 13.3 microprocessor-stance-and-swing-phase-controlled-knee-ankle-foot orthoses (MP-SSCOs) since product availability participated. Reported underlying conditions comprised incomplete paraplegia (18%), peripheral nerve lesions (20%), poliomyelitis (41%), post-traumatic lesions (8%) and other disorders (13%). The leading observed patient burdens were "restriction of mobility" (n=6), followed by "emotional strain" (n=5) and "impaired gait pattern" (n=4). Corresponding results for potential patient benefits were seen in "improved quality-of-life" (n=8) as well as "improved gait pattern" (n=8) followed by "high reliability of the orthosis" (n=7). In total, experts reported falls occurring in 71.5% of patients at a combined annual frequency of 7.0 fall events per year when using KAFOs or stance control orthoses (SCOs). In contrast, falls were observed in only 7.2 % of MPSSCO users.
Conclusion: Advanced orthotic technology might contribute to better quality of life of patients, improved gait pattern and perceived reliability of orthosis. In terms of safety a substantial decrease in frequency of falls was observed when comparing KAFO and MP-SSCO users.
Keywords: Ankle Foot Orthoses; KAFO; Knee Instability; MP-SCCOs; Microprocessor Orthoses; Patient Burden; Poliomyelitis; Quality of Life; Survey.
Copyright (c) 2022 Brüggenjürgen B., Braatz F., Greitemann B., Drewitz H., Ruetz A., Schäfer M., et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Bernd Brüggenjürgen, Frank Braatz, Bernhard Greitemann, Axel Ruetz, Friedemann Steinfeldt, Daiwei Yao, and Christina Stukenborg-Colsman received lecture fees; Heiko Drewitz is an employee of Otto Bock; Michael Schäfer, Wolfgang Seifert have collaborations with the sponsor. Claudia Weichold none to be declared.
Figures

References
-
- O’Connor J, McCaughan D, McDaid C, Booth A, Fayter D, Rodriguez-Lopez R, et al.. Orthotic management of instability of the knee related to neuromuscular and central nervous system disorders: systematic review, qualitative study, survey and costing analysis. Health technology assessment. 2016;20(55):1-262. DOI: 10.3310/hta20550 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fox JR, Lovegreen W. 22 - Lower Limb Orthoses. In: Webster JB, Murphy DP, editors. Atlas of Orthoses and Assistive Devices (Fifth Edition). Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2019; 239-46.e1.
-
- McDaid C, Fayter D, Booth A, O’Connor J, Rodriguez-Lopez R, McCaughan D, et al.. Systematic review of the evidence on orthotic devices for the management of knee instability related to neuromuscular and central nervous system disorders. BMJ Open. 2017;7(9):e015927. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-015927 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
