Extensive Cardiac Function Analyses Using Contemporary Echocardiography in Childhood Cancer Survivors: A DCCSS LATER Study
- PMID: 37614574
- PMCID: PMC10443197
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2023.06.003
Extensive Cardiac Function Analyses Using Contemporary Echocardiography in Childhood Cancer Survivors: A DCCSS LATER Study
Abstract
Background: Childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at risk for cardiotoxicity.
Objectives: We sought to assess how cardiac dysfunction measurements in CCS overlap and are differentially influenced by risk factors.
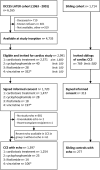
Methods: This cross-sectional Dutch Childhood Cancer Survivor Study evaluated echocardiograms of 1,397 ≥5-year CCS and 277 siblings. Of CCS, n = 1,254 received cardiotoxic (anthracyclines/mitoxantrone/radiotherapy involving the heart region [RTheart]) and n = 143 received potentially cardiotoxic (cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, or vincristine) therapy. We assessed demographic, treatment-related, and traditional cardiovascular risk factors for cardiac dysfunction using multivariable logistic regression.
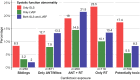
Results: CCS were a median of 26.7 years after diagnosis; 49% were women. Abnormal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (defined as <52% in men, <54% in women) occurred most commonly in CCS treated with anthracyclines and RTheart combined (38%). Age/sex-specific abnormal global longitudinal strain (GLS) occurred most commonly in CCS treated with RTheart, either with (41%) or without (38%) anthracyclines. Of CCS with normal LVEF, 20.2% showed abnormal GLS. Diastolic dysfunction grade ≥II was rare. Abnormal LVEF was mainly associated with female sex, anthracycline dose, and only in women, RTheart dose. Abnormal GLS was associated with female sex, RTheart dose, diastolic blood pressure, and only in women, anthracycline dose. Cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, and vincristine were not associated with LVEF or GLS. Compared with siblings, CCS showed higher risk of abnormal LVEF (OR: 2.9; 95% CI: 1.4-6.6) and GLS (OR: 2.1; 95% CI: 1.2-3.7), independent of (potentially) cardiotoxic treatment-related and cardiovascular risk factors.
Conclusions: Abnormal LVEF and GLS constitute complementary measures of systolic dysfunction among long-term CCS. Their diagnostic value may differ according to cardiotoxic exposures. Also, CCS have residual, unexplained risk of cardiac dysfunction. (Early Detection of Cardiac Dysfunction in Childhood Cancer Survivors, a DCOG LATER study; NTR7481).
Keywords: cancer survivors; cardiotoxicity; child; echocardiography; global longitudinal strain; left ventricular dysfunction.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by grant CVON 2015-021 of the Dutch Heart Foundation and grant 171 DCOG LATER program of KiKa and ODAS. The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cardiac function in childhood cancer survivors treated with vincristine: Echocardiographic results from the DCCSS LATER 2 CARD study.Int J Cardiol. 2022 Dec 15;369:69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2022.07.049. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Int J Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35926643
-
Echocardiography protocol for early detection of cardiac dysfunction in childhood cancer survivors in the multicenter DCCSS LATER 2 CARD study: Design, feasibility, and reproducibility.Echocardiography. 2021 Jun;38(6):951-963. doi: 10.1111/echo.15081. Epub 2021 May 20. Echocardiography. 2021. PMID: 34013999 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac and obstetric outcomes of pregnancies for women after cardiotoxic therapy in childhood: a single center observational study.BMC Cancer. 2023 Feb 2;23(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10578-y. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36732710 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Myocardial Strain Imaging in Cancer Therapy-Related Cardiac Dysfunction.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2022 Jun;24(6):739-748. doi: 10.1007/s11886-022-01692-7. Epub 2022 May 6. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35522421 Review.
-
Assessment of Prognostic Value of Left Ventricular Global Longitudinal Strain for Early Prediction of Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Oct 1;4(10):1007-1018. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.2952. JAMA Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31433450 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pediatric Cardio-Oncology: Screening, Risk Stratification, and Prevention of Cardiotoxicity Associated with Anthracyclines.Children (Basel). 2024 Jul 22;11(7):884. doi: 10.3390/children11070884. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39062333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time course of hypertension and myocardial dysfunction following anthracycline chemotherapy in pediatric patients.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024 May 31;53:101436. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101436. eCollection 2024 Aug. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024. PMID: 38872982 Free PMC article.
-
Rurality, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and Early Cardiovascular Disease among Childhood, Adolescent, and Young Adult Cancer Survivors.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 1:rs.3.rs-4139837. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4139837/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: J Adolesc Young Adult Oncol. 2025 Mar 25. doi: 10.1089/jayao.2024.0151. PMID: 38645102 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Predicting Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Childhood Cancer Survivors: In Search of the Echocardiography Holy Grail.JACC CardioOncol. 2023 Aug 15;5(4):486-488. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2023.07.003. eCollection 2023 Aug. JACC CardioOncol. 2023. PMID: 37614572 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular health in pediatric patients with X-linked hypophosphatemia under two years of burosumab therapy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 May 16;15:1400273. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1400273. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38818505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thavendiranathan P., Grant A.D., Negishi T., Plana J.C., Popovic Z.B., Marwick T.H. Reproducibility of echocardiographic techniques for sequential assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction and volumes: application to patients undergoing cancer chemotherapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:77–84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

