Renal vascular responses to angiotensin II infusion in two kidneys-one clip hypertensive rats under partial ischemia/reperfusion with and without ischemia preconditioning: the roles of AT1R blockade and co-blockades of AT1R and MasR
- PMID: 37614612
- PMCID: PMC10443668
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.378086
Renal vascular responses to angiotensin II infusion in two kidneys-one clip hypertensive rats under partial ischemia/reperfusion with and without ischemia preconditioning: the roles of AT1R blockade and co-blockades of AT1R and MasR
Abstract
Background and purpose: The renin-angiotensin system activation, partial ischemia/reperfusion (IR) injury, and hypertension contribute to the development of acute kidney injury. The study aims to look at the vascular responses of angiotensin II (Ang II) during Ang II type 1 receptor (AT1R) blockade (losartan) or co-blockades of AT1R and Mas receptor (A779) in two kidneys one clip (2K1C) hypertensive rats which subjected to partial IR injury with and without ischemia preconditioning (IPC).
Experimental approach: Thirty-three 2K1C male Wistar rats with systolic blood pressure ≥ 150 mmHg were divided into three groups of sham, IR, and IPC + IR divided into two sub-groups receiving losartan or losartan + A779. The IR group had 45 min partial kidney ischemia, while the IPC + IR group had two 5 min cycles of partial ischemia followed by 10 min of reperfusion and then 45 min of partial kidney ischemia followed by reperfusion. The sham group was subjected to similar surgical procedures except for IR or IPC.
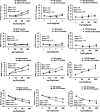
Findings/results: Ang II increased mean arterial pressure in all the groups, but there were no significant differences between the sub-groups. A significant difference was observed in the renal blood flow response to Ang II between two sub-groups of sham and IR groups treated with AT1R blockade alone or co-blockades of AT1R + A779.
Conclusion and implications: These findings demonstrated the significance of AT1R and Mas receptor following partial renal IR in the renal blood flow responses to Ang II in 2K1C hypertensive rats.
Keywords: AT1R; Angiotensin II; MasR; Renal ischemia/reperfusion; Two kidneys-one clip.
Copyright: © 2023 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mas Receptor Blockade Promotes Renal Vascular Response to Ang II after Partial Kidney Ischemia/Reperfusion in a Two-Kidney-One-Clip Hypertensive Rats Model.Int J Nephrol. 2021 Apr 20;2021:6618061. doi: 10.1155/2021/6618061. eCollection 2021. Int J Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33986960 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Vascular Response to Angiotensin II Administration in Two Kidneys-One Clip Hypertensive Rats Treated with High Dose of Estradiol: The Role of Mas Receptor.Int J Vasc Med. 2021 Mar 1;2021:6643485. doi: 10.1155/2021/6643485. eCollection 2021. Int J Vasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33747565 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in the Renal Vascular Responses of AT1 and Mas Receptors in Two-Kidney-One-Clip Hypertension.Int J Hypertens. 2021 Feb 20;2021:8820646. doi: 10.1155/2021/8820646. eCollection 2021. Int J Hypertens. 2021. PMID: 33688433 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin 2 type 1 receptor blockade different affects postishemic kidney injury in normotensive and hypertensive rats.J Physiol Biochem. 2016 Dec;72(4):813-820. doi: 10.1007/s13105-016-0514-4. Epub 2016 Aug 18. J Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27534651 Review.
-
View of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Acute Kidney Injury Induced by Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2022 Oct 22;2022:9800838. doi: 10.1155/2022/9800838. eCollection 2022. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2022. PMID: 36320442 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antagonist on Age-Related Differences in Renal Vascular Responses to Angiotensin II in Male and Female Rats.Adv Biomed Res. 2024 Aug 26;13:71. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_387_23. eCollection 2024. Adv Biomed Res. 2024. PMID: 39434945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karimi F, Kasaei S, Baradaran A, Ashrafi F, Talebi A, Lak Z, et al. Dextrose hydration may promote cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: gender-related difference. Indones Biomed J. 2019;11(2):136–144. DOI: 10.18585/inabj.v11i2.502.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
