Design of a 6-DoF Parallel Robotic Platform for MRI Applications
- PMID: 37614779
- PMCID: PMC10445425
- DOI: 10.1142/s2424905x22410057
Design of a 6-DoF Parallel Robotic Platform for MRI Applications
Abstract
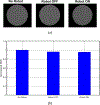
In this work, the design, analysis, and characterization of a parallel robotic motion generation platform with 6-degrees of freedom (DoF) for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) applications are presented. The motivation for the development of this robot is the need for a robotic platform able to produce accurate 6-DoF motion inside the MRI bore to serve as the ground truth for motion modeling; other applications include manipulation of interventional tools such as biopsy and ablation needles and ultrasound probes for therapy and neuromodulation under MRI guidance. The robot is comprised of six pneumatic cylinder actuators controlled via a robust sliding mode controller. Tracking experiments of the pneumatic actuator indicates that the system is able to achieve an average error of 0.69 ± 0.14 mm and 0.67 ± 0.40 mm for step signal tracking and sinusoidal signal tracking, respectively. To demonstrate the feasibility and potential of using the proposed robot for minimally invasive procedures, a phantom experiment was performed in the benchtop environment, which showed a mean positional error of 1.20 ± 0.43 mm and a mean orientational error of 1.09 ± 0.57°, respectively. Experiments conducted in a 3T whole body human MRI scanner indicate that the robot is MRI compatible and capable of achieving positional error of 1.68 ± 0.31 mm and orientational error of 1.51 ± 0.32° inside the scanner, respectively. This study demonstrates the potential of this device to enable accurate 6-DoF motions in the MRI environment.
Keywords: MRI; motion generation; parallel robot.
Figures




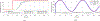

Similar articles
-
An MRI-Guided Telesurgery System Using a Fabry-Perot Interferometry Force Sensor and a Pneumatic Haptic Device.Ann Biomed Eng. 2017 Aug;45(8):1917-1928. doi: 10.1007/s10439-017-1839-z. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017. PMID: 28447178 Free PMC article.
-
Piezoelectrically Actuated Robotic System for MRI-Guided Prostate Percutaneous Therapy.IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2015 Aug;20(4):1920-1932. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2014.2359413. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2015. PMID: 26412962 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a 3D parallel mechanism robot arm with three vertical-axial pneumatic actuators combined with a stereo vision system.Sensors (Basel). 2011;11(12):11476-94. doi: 10.3390/s111211476. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Sensors (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22247676 Free PMC article.
-
A Fully Actuated Robotic Assistant for MRI-Guided Precision Conformal Ablation of Brain Tumors.IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2021;26(1):255-266. doi: 10.1109/tmech.2020.3012903. Epub 2020 Jul 29. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2021. PMID: 33994771 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of six degree-of-freedom high-precision robotic phantom on commercial industrial robotic manipulator.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2021 Aug 9;7(5). doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/ac1988. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2021. PMID: 34330110
Cited by
-
Modeling and Control of an MR-Safe Pneumatic Radial Inflow Motor and Encoder (PRIME).IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2024 Jun;29(3):1714-1725. doi: 10.1109/tmech.2023.3329296. Epub 2023 Dec 13. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2024. PMID: 38895598 Free PMC article.
-
Open Source MR-Safe Pneumatic Radial Inflow Motor and Encoder (PRIME): Design and Manufacturing Guidelines.Int Symp Med Robot. 2023 Apr;2023:10.1109/ismr57123.2023.10130240. doi: 10.1109/ismr57123.2023.10130240. Epub 2023 May 25. Int Symp Med Robot. 2023. PMID: 38073863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Musa M, Sengupta S and Chen Y, MRI-compatible soft robotic sensing pad for head motion detection, IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett 7(2) (2022) 3632–3639.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
