The Role of Gut Microbiome in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37614827
- PMCID: PMC10442465
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.43862
The Role of Gut Microbiome in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review
Abstract
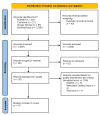
Gut microbiome dysbiosis is common in patients with chronic liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and plays an essential role in developing, diagnosing, and treating HCC. The purpose of this systematic review, which was carried out following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analyses 2020 guidelines, is to determine the role of the gut microbiome in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of HCC. We collected and reviewed articles, including clinical trials, literature reviews, case-control studies, cross-sectional studies, cohort studies, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses, published between May 30, 2013, and May 30, 2023. The databases used to collect these articles included PubMed, Cochrane Library, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect. After applying appropriate filters, a total of 2,969 studies were identified. They were further screened and subjected to quality assessment tools which finally yielded 17 studies included in this systematic review. This systematic review provides information regarding the gut-liver axis and the relationship between gut microbiome dysbiosis and HCC.
Keywords: gastrointestinal microbiome; gut flora; gut microbiome; hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc); liver cancer.
Copyright © 2023, Trivedi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Gut Microbiome in Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2022 Dec 13;14(12):e32465. doi: 10.7759/cureus.32465. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36644080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbial Dysbiosis in the Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2020 Apr;120(4):565-586. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2019.05.015. Epub 2019 Aug 28. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2020. PMID: 31473156
-
Contribution of the Gut Microbiome to the Perpetuation of Inflammation in Crohn's Disease: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Aug 24;16(8):e67672. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67672. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39314611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Development of Levosimendan in Acute and Advanced Heart Failure: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Apr 19;15(4):e37844. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37844. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37214028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential relationship of the gut microbiome with testosterone level in men: a systematic review.PeerJ. 2025 Apr 15;13:e19289. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19289. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40256744 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Intestinal Microbiome Associated with Efficacy of Atezolizumab and Bevacizumab Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 26;16(9):1675. doi: 10.3390/cancers16091675. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38730627 Free PMC article.
-
Liver, ageing and disease.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jul 28. doi: 10.1038/s41575-025-01099-z. Online ahead of print. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40721658 Review.
-
Understanding the role of Hedgehog signaling pathway and gut dysbiosis in fueling liver cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Apr 22;52(1):411. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10504-4. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40261446 Review.
-
Gut Microbiota, Deranged Immunity, and Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 7;12(8):1797. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081797. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Gut Microbial Metabolites in the Pathogenesis of Primary Liver Cancers.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 22;16(14):2372. doi: 10.3390/nu16142372. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064815 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Part 1: the human gut microbiome in health and disease. Bull MJ, Plummer NT. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4566439/ Integr Med (Encinitas) 2014;13:17–22. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources