Severe gastrointestinal involvement in pediatric IgA vasculitis: a retrospective single-center cohort study in China
- PMID: 37614903
- PMCID: PMC10442948
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2023.1194214
Severe gastrointestinal involvement in pediatric IgA vasculitis: a retrospective single-center cohort study in China
Abstract
Objectives: The study aimed to describe the characteristics of gastrointestinal (GI) involvement in a cohort of hospitalized children with IgA vasculitis (IgAV) in China.
Method: We reviewed the records of hospitalized IgAV patients from January 2014 to December 2020 at one tertiary medical center. The patients were divided into the severe GI group and the non-severe GI group according to the presence of massive GI bleeding and complications. The clinical manifestations, laboratory factors, and treatment were analyzed between the two groups.
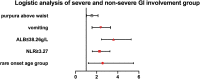
Results: A total of 1,179 patients were hospitalized due to IgAV. GI involvement was noted in 50% (589) of the patients, of whom 288 (48.9%) had severe GI involvement. GI complications were observed in 34 patients with IgAV with GI involvement. Rare onset age (<3 years or within 13-17 years), purpura above the waist, vomiting, high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and decreased serum albumin were factors associated with severe GI involvement. Frequencies of renal involvement and biopsy-proven nephritis were higher in the severe GI group. The most commonly used medications were corticosteroids (100.0%) in the severe GI group. The maximum corticosteroid dose was higher (2.9 vs. 2.0 mg/kg), and more second-line therapies were needed (30.9% vs. 16.94%) in the severe GI group.
Conclusions: Severe GI involvement in children is common in our center. Rare onset age, purpura above the waist, vomiting, high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and decreased serum albumin are associated with severe GI involvement. Patients with severe GI involvement need higher doses of corticosteroids and second-line therapy.
Keywords: IgA vasculitis; gastrointestinal involvement; pediatric; severe; treatment.
© 2023 Li, Zhang, Liu, Li, Guan, Zhang, Zeng, Gong, Xu and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gastrointestinal involvement in IgA vasculitis: a single-center 11-year study on a cohort of 118 children.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Dec;40(12):5041-5046. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05863-9. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34273001
-
Gastrointestinal involvement and its association with the risk for nephritis in IgA vasculitis.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021 Jun 30;13:1759720X211024828. doi: 10.1177/1759720X211024828. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021. PMID: 34262620 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting gastrointestinal and renal involvement in adult IgA vasculitis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Dec 26;21(1):302. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-2089-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31878954 Free PMC article.
-
IgA vasculitis.Semin Immunopathol. 2021 Oct;43(5):729-738. doi: 10.1007/s00281-021-00874-9. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Semin Immunopathol. 2021. PMID: 34170395 Review.
-
Penile involvement of immunoglobulin a vasculitis/Henoch-Schönlein purpura.J Pediatr Urol. 2021 Jun;17(3):409.e1-409.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2021.01.012. Epub 2021 Jan 22. J Pediatr Urol. 2021. PMID: 33558175 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunoglobulin a vasculitis with central nervous system involvement: analysis of 10 cases.Clin Exp Med. 2025 May 9;25(1):145. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01679-y. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40346320 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of cutaneous manifestations in immunoglobulin a vasculitis and their relationships with system involvement and treatment needs.Eur J Pediatr. 2024 Nov 15;184(1):17. doi: 10.1007/s00431-024-05824-9. Eur J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39546045
-
Gastrointestinal features of pediatric iga vasculitis and their association with renal complications: an observational study.Eur J Pediatr. 2025 May 1;184(5):320. doi: 10.1007/s00431-025-06157-x. Eur J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40310537 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features and risk factors of abdominal IgA vasculitis in adults.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jul 11. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07569-8. Online ahead of print. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40646367
-
Predictors of Gastrointestinal Involvement in Children with IgA Vasculitis: Results from a Single-Center Cohort Observational Study.Children (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;11(2):215. doi: 10.3390/children11020215. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397327 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous