Uptake, Safety and Attitudes Towards COVID-19 Vaccination: A Cross-Sectional Study on First and Second Doses Among the General Public
- PMID: 37614963
- PMCID: PMC10443679
- DOI: 10.2147/RMHP.S418300
Uptake, Safety and Attitudes Towards COVID-19 Vaccination: A Cross-Sectional Study on First and Second Doses Among the General Public
Abstract
Objective: To investigate public uptake, attitudes and the safety of the first and second doses of COVID-19 vaccination.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional web-based survey study. A self-administered questionnaire was prepared from a literature search and information about COVID-19 available at various resources. The developed questionnaire was validated for readability by experts and refined in light of the feedback received from the experts and the final version was prepared. The reliability of the questionnaire was 0.7 which shows an acceptable level of scale internal consistency. The data analysis was performed using IBM SPSS software (version 25).
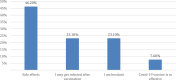
Results: A total of 513 participants completed the survey, including 311 (60.6%) women and 202 (39.4%) men. The mean age was (31.5±12.8) years. It was found that 493 (96.1%) took the first and second doses of COVID-19 and 376 (73.3%) suffered from side effects, of these 14% (56/376) reported the side effects to the health authorities. The most common side effects were fatigue (51.5%), fever (42.3%), headache (39.5%), and injection site pain (37.6%). Half of the participants (50.5%) had a positive attitude towards COVID-19 preventive measures. Females had higher odds of experiencing side effects than males OR (95% CI); 2.002 (1.312-3.056). Individuals living in urban areas had lower odds of experiencing side effects than those living in rural areas OR (95% CI); 0.364 (0.142-0.933).
Conclusion: Vaccine uptake was massive and side effects due to the COVID-19 vaccine were common but minor. The majority of the participants had positive attitudes towards recommended COVID-19 preventive measures. Being female and living in rural areas were associated with experiencing side effects.
Keywords: COVID-19; safety; uptake.
© 2023 Mahmoud et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A First Report on Side-Effects of COVID-19 Vaccines among General Population in Sudan: A Cross-Sectional Analysis.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;11(2):315. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020315. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851192 Free PMC article.
-
Side effects of Pfizer/BioNTech (BNT162b2) COVID-19 vaccine reported by the Birzeit University community.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Jan 5;23(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07974-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36604613 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Short-Term Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines: A Cross-Sectional Study on Vaccinated People in the UAE.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Dec 15;10(12):2157. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10122157. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560566 Free PMC article.
-
Surveillance of Side Effects after Two Doses of COVID-19 Vaccines among Patients with Comorbid Conditions: A Sub-Cohort Analysis from Saudi Arabia.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Dec 6;58(12):1799. doi: 10.3390/medicina58121799. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36557002 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination coverage among COVID-19 prevention and control management teams at primary healthcare facilities in China and their attitudes towards COVID-19 vaccine: a cross-sectional online survey.BMJ Open. 2022 Apr 7;12(4):e056345. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-056345. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35393315 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring the relationship between experience of vaccine adverse events and vaccine hesitancy: A scoping review.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025 Dec;21(1):2471225. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2471225. Epub 2025 Mar 9. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40058398 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard: overview; 2023. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/?adgroupsurvey=%7Badgroupsurvey%7D&gclid=Cj0KCQi.... Accessed March 7, 2023.
-
- World Health Organization. Saudi Arabia Situation on COVID-19; 2022. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/region/emro/country/sa. Accessed August 5, 2022.
-
- COVID-19 vaccine tracker. Saudi Arabia; 2022. Available from https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/country/saudi-arabia/. Accessed August 19, 2022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources