In-Office Suprachoroidal Viscopexy for Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Repair
- PMID: 37615957
- PMCID: PMC10587788
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2023.3785
In-Office Suprachoroidal Viscopexy for Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Repair
Abstract
Importance: In-office suprachoroidal viscopexy (SCVEXY) is a minimally invasive technique for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD) repair that can be performed with no incision, no tamponade agent, and no positioning requirements. This technique has the potential to be a step forward in the armamentarium to treat RRDs.
Objective: To describe in-office SCVEXY for RRD repair.
Design, setting, and participant: In this single-case report with short follow-up, a man in his 50s with pseudophakia and recent visual loss presented to St Michael's Hospital, Unity Health Toronto, with a fovea-off RRD in the right eye, extending from 6 to 10 o'clock, with no visible causative retinal break.
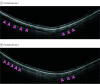
Exposure: Injection of suprachoroidal sodium hyaluronate, 1%, in the region of the suspected break, using a 30-gauge needle with a custom-made guard that exposed only 1 mm of the needle.
Main outcome and measures: Ability to perform in-office SCVEXY and to obtain a visible choroidal indentation.
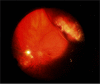
Results: After the procedure, a dome-shaped choroidal convexity was present in the superior temporal area. The patient achieved macular reattachment in less than 24 hours with no postoperative abnormalities, such as outer retinal folds, residual subfoveal fluid, or retinal displacement, with rapid recovery of the outer retinal bands on optical coherence tomography. The optical coherence tomography scans acquired in the area of the choroidal convexity demonstrated the location of the viscoelastic material in the suprachoroidal space. Laser retinopexy was applied in the suspected region of the retinal tear, and the patient was able to resume normal activity immediately after the procedure with no restrictions.
Conclusions and relevance: Suprachoroidal viscopexy is feasible as an in-office technique to create a temporary choroidal buckle for RRD repair. It is a minimally invasive procedure with the potential to maximize anatomical outcomes of integrity and postoperative functional outcomes in RRD because its mechanism of action does not require drainage of subretinal fluid or intraocular gas tamponade. Nevertheless, this was a single-case report with short follow-up, which limits the ability to determine the procedure's benefits, potential adverse events, failure rates, and best-case selection. Further work is required to refine the procedure and assess its efficacy and safety.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
In-Office Suprachoroidal Viscopexy for Acute Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2025 Jan 1;143(1):53-60. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.5202. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39666366
-
Pneumatic Retinopexy Rescue with In-Office Suprachoroidal Viscopexy (SCVEXY).Retina. 2025 Feb 26. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000004439. Online ahead of print. Retina. 2025. PMID: 40030128
-
Choroidal Thickness Is Associated with Delayed Subretinal Fluid Absorption after Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Surgery.Ophthalmol Retina. 2019 Nov;3(11):947-955. doi: 10.1016/j.oret.2019.05.009. Epub 2019 May 15. Ophthalmol Retina. 2019. PMID: 31324589
-
Face-down positioning or posturing after pars plana vitrectomy for macula-involving rhegmatogenous retinal detachments.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Mar 15;3(3):CD015514. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015514.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38488250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pars plana vitrectomy versus scleral buckling for repairing simple rhegmatogenous retinal detachments.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 8;3(3):CD009562. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009562.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30848830 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In-Office Suprachoroidal Viscopexy for Acute Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2025 Jan 1;143(1):53-60. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.5202. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39666366
References
-
- Williams GA, Aaberg TA Jr. Techniques of scleral buckling. In: Ryan SJ, Wilkinson CP, eds. Retina . Vol 3. 4th ed. Elsevier Mosby; 2006:2035-2207.
-
- Heimann H, Hellmich M, Bornfeld N, Bartz-Schmidt KU, Hilgers RD, Foerster MH. Scleral buckling versus primary vitrectomy in rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (SPR Study): design issues and implications. SPR Study report no. 1. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2001;239(8):567-574. doi:10.1007/s004170100319 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

