Islet beta-cells and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1): Integrating immune responses that influence autoimmunity and graft rejection
- PMID: 37619906
- PMCID: PMC10543623
- DOI: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103414
Islet beta-cells and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1): Integrating immune responses that influence autoimmunity and graft rejection
Abstract
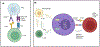
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) develops due to autoimmune targeting of the pancreatic islet β-cells. Clinical symptoms arise from reduced insulin in circulation. The molecular events and interactions between discrete immune cell populations, infiltration of such leukocytes into pancreatic and islet tissue, and selective targeting of the islet β-cells during autoimmunity and graft rejection are not entirely understood. One protein central to antigen presentation, priming of immune cells, trafficking of leukocytes, and vital for leukocyte effector function is the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). The gene encoding ICAM-1 is transcriptionally regulated and rapidly responsive (i.e., within hours) to pro-inflammatory cytokines. ICAM-1 is a transmembrane protein that can be glycosylated; its presence on the cell surface provides co-stimulatory functions for immune cell activation and stabilization of cell-cell contacts. ICAM-1 interacts with the β2-integrins, CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1) and CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1), which are present on discrete immune cell populations. A whole-body ICAM-1 deletion protects NOD mice from diabetes onset, strongly implicating this protein in autoimmune responses. Since several different cell types express ICAM-1, its biology is fundamentally essential for various physiological and pathological outcomes. Herein, we review the role of ICAM-1 during both autoimmunity and islet graft rejection to understand the mechanism(s) leading to islet β-cell death and dysfunction that results in insufficient circulating quantities of insulin to control glucose homeostasis.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; ICAM-1; Inflammation; Pancreatic islet; Type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Jason Collier reports financial support was provided by National Institutes of Health.
Figures
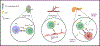
Similar articles
-
Competition between lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (CD11a/CD18) and Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) for binding to intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (CD54).J Leukoc Biol. 1996 May;59(5):648-55. doi: 10.1002/jlb.59.5.648. J Leukoc Biol. 1996. PMID: 8656049
-
Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 on pancreatic beta-cells accelerates beta-cell destruction by cytotoxic T-cells in murine autoimmune diabetes.Diabetes. 1995 Jul;44(7):744-52. doi: 10.2337/diab.44.7.744. Diabetes. 1995. PMID: 7789642
-
Human leukaemic (HMC-1) and normal skin mast cells express beta 2-integrins: characterization of beta 2-integrins and ICAM-1 on HMC-1 cells.Scand J Immunol. 1997 May;45(5):471-81. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1997.d01-420.x. Scand J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9160089
-
Differential expression of ICAM-1 and LFA-1 versus L-selectin and VCAM-1 in autoimmune insulitis of NOD mice and association with both Th1- and Th2-type infiltrates.J Autoimmun. 1996 Oct;9(5):637-43. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1996.0083. J Autoimmun. 1996. PMID: 8933279
-
Inhibition of LFA-1/ICAM-1 and VLA-4/VCAM-1 as a therapeutic approach to inflammation and autoimmune diseases.Med Res Rev. 2002 Mar;22(2):146-67. doi: 10.1002/med.10001. Med Res Rev. 2002. PMID: 11857637 Review.
Cited by
-
Accelerated onset of diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice fed a refined high-fat diet.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024 Jun;26(6):2158-2166. doi: 10.1111/dom.15522. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024. PMID: 38433703 Free PMC article.
-
ITGAL expression in non-small-cell lung cancer tissue and its association with immune infiltrates.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 4;15:1382231. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1382231. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38646528 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the apoptotic markers Apo1/Fas and cCK-18 and the adhesion molecule ICAM-1 with Type 1 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Aug 2;24(1):493. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-04926-5. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39095736 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Multi-PTM Proteomics Reveals Dynamic Global, Redox, Phosphorylation, and Acetylation Regulation in Cytokine-Treated Pancreatic Beta Cells.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2024 Dec;23(12):100881. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2024.100881. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 39550035 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the pathogenic interplay between SARS-CoV-2 and polycystic ovary syndrome using bioinformatics and experimental validation.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 2;14(1):22934. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74347-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39358491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kahn BB, Type 2 diabetes: when insulin secretion fails to compensate for insulin resistance, Cell 92 (1998) 593–6. - PubMed
-
- Esser N, Utzschneider KM and Kahn SE, Early beta cell dysfunction vs insulin hypersecretion as the primary event in the pathogenesis of dysglycaemia, Diabetologia 63 (2020) 2007–2021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

